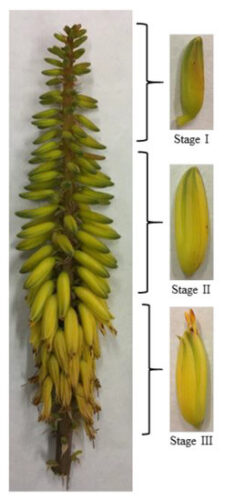
Before they are ready to bloom, aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) flowers go through a number of stages of growth. The three stages of flower development—St. Aloe I (young), St. Aloe II (mature but with closed flower buds), and St. Aloe III—have been the subject of research on the bioactivity of aloe vera flowers.
Aloe vera buds often begin to develop in the winter, when temperatures are at their lowest and days are shorter, allowing the plant to get less sunlight. The flower buds are now beginning to assemble. The plant enters the second stage as it becomes older, when the flower buds are still closed but almost ready.
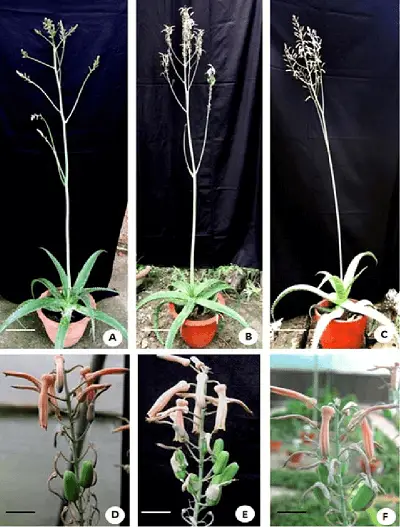
Aloe vera trees have a lifespan of 5 to 25 years or even more, depending on their growth conditions. The plant may begin to bloom when it reaches a particular age, generally at least four years old. The stalk from which the flowers emerge rises above the plant’s lovely rosettes. On a mature plant, at least one raceme—a cluster of flowers—can develop annually. It could potentially have many blooms in a single growth season.
In most cases, aloe vera only experiences its blooming stage once each year, from early spring until summer. The plant is growing the most at this time. But depending on a variety of factors, the precise period of blooming may vary.
It’s vital to note that the Aloe Vera plant is only available in the United States. The plant typically needs four years to reach the stage of growth required to produce flowers. The plant may sometimes take longer to bloom, therefore it’s crucial to keep in mind that this time period is subject to change.
The chemical make-up of the Aloe Vera plant has been studied by researchers, and it has been shown to be effective. At each stage of floral growth, including stage I (young), stage II (mature), and stage III (mature with open flower buds), total phenolic compounds have been examined.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Germination | Aloe vera seeds germinate in moist, warm soil. A seed root emerges, anchoring the young plant, while embryonic leaves grow upward. |
| Growth | A rosette of fleshy leaves with a jelly-like pulp and sap emerges. Leaves have spines for protection. A mature Aloe vera plant can reach a height and width of approximately 24 inches. |
| Flowering | In late winter to midsummer, a tall flower spike emerges from the center of the leaf rosette. Small, yellow, tubular flowers appear at the tip. Pollination occurs naturally or by other species of hummingbirds. |
| Seed Production | Pollinated flowers develop into green pods that mature, dry out, and split open to release seeds into the soil. Seeds remain dormant until optimal conditions for germination are met. |
| Death | Aloe vera plants have a lifespan of 5 to 25 years or longer. Environmental stresses, such as frost, animal consumption, drought, or fungal rot from flooding, can lead to the plant’s demise. |
The Life Cycle of an Aloe Vera Plant
Sprouting, growth, blooming, seed production, and death are just a few of the stages that an Aloe Vera plant goes through throughout its existence. You may have a better understanding of how this plant has developed and altered through time by studying about these phases.
Aloe vera seeds have a remarkable capacity to germinate when placed in warm, wet soil. When the circumstances are ideal, a root develops from the seed and descends to support the young plant. The earliest, small leaves, which are establishing the foundation for future growth, begin to climb upward in the meantime.
- Growth: The young Aloe vera plant produces a large number of thick, pointed leaves at the height of the growth season. These leaves contain a sap and pulp that resemble jelly and aid in the health and wound healing of the plant. To defend the plant from animals seeking food and water, the leaf tips develop spines. The leaf cells maintain their strength and fullness as long as the temperature doesn’t drop below freezing for extended periods of time. Aloe vera plants may reach heights and widths of up to 24 inches when fully established. Small, vegetative “pups” that grow adjacent to the mother plant at the base of the plant. These “pups” eventually unite to produce a large, clumped mass of Aloe plants.
- Flowering: In late winter or early summer, depending from the climate, a mature Aloe vera plant will shoot up a long, thin flower spike from the middle of its leaf cluster. A cluster of tiny, tubular, yellow flowers are seen at the tip of this spike. Finches pollinate the flowers of Africa where they grow there organically. However, several hummingbird species perform the task of fertilization outside of their normal habitat. Fertilization isn’t always beneficial since the partners don’t know each other well.
- The pollinated flowers develop into little green pods with grooves that resemble chubby cucumbers. These pods age, dry up, and eventually become brown. The seeds eventually break open and fall to the ground. As long as the seeds remain latent until the conditions are suitable for them to sprout, the Aloe vera plant’s life cycle will continue.
- Death: Aloe vera trees have a lifespan of 5 to 25 years, if not more, depending on the growth environment. Due to the fact that the mother plants produce both young plants and seeds, several Aloe vera plants grow close to one another. These plants often perish as a result of extreme weather conditions, such as a hard frost, animals devouring them, or a protracted drought that causes them to lose all of their water. Flooding may also result in fungal rot, which accelerates the demise of an Aloe vera plant.

We can understand how resilient and adaptable the Aloe vera plant is by examining its life cycle. The plant passes through the stages of blooming and producing seeds, making sure that its lineage will continue, from the moment the seeds sprout until the time they create robust leaves. The capacity to generate new plants from pups and seeds is a key component of the aloe vera plant’s success, and it’s no surprise that the aloe vera plant’s popularity is growing.
How Long Does It Take for an Aloe Vera Flower to Bloom?
Aloe vera trees are notorious for growing slowly, and it often takes them some time before they are large enough to bloom. Flowering usually takes place in the third or fourth year of an aloe vera plant’s existence. Prior to this, the plant concentrates its energy on developing roots and leaf growth.
An aloe vera plant typically produces at least one raceme every year after it reaches maturity. It may even bloom twice or more throughout a growing season in rare situations. Aloe vera flowers may bloom at various periods, depending on the climate and surroundings. Aloes normally bloom in zones 9–11 from March through April, while in zones 10–12, blooming occurs throughout the summer.
The color of the flowers of the Aloe Vera plant is red, while the plant’s leaves are green. The Aloe Vera plant is a good example of a plant that may be used to make a flower. The aloe vera plant looks attractive thanks to these vibrant flowers, which also attract bees and butterflies.
Keep in mind that not all mature aloe vera plants will reproduce. Some factors, such as inadequate sunshine or poor plant care, might prevent the plant from blossoming. Aloe vera plant flowering may sometimes be difficult to achieve as well. However, if you give your aloe vera plant the proper attention, such as sufficient sunshine, well-draining soil, and the perfect quantity of water, you may raise the likelihood that it will produce flowers.
What to do when aloe vera starts flowering?
Seeing your aloe vera plant bloom is thrilling and lovely. Aloe vera flowers resemble the vibrant blooms of Red Hot Poker plants. On a sturdy flower stem, they feature a long cluster of yellow and orange flowers. However, it’s crucial to keep in mind that both blooming and non-flowering aloe vera plants need the same level of maintenance.
It is preferable to remove the flower stem when the petals start to fall off and the flowers begin to dry up. In order to expand and develop in the future, the plant may store energy in this way. You may encourage the aloe vera plant to produce new leaves and maintain overall health by chopping off the dried flower stem.
In order to remain healthy, flowering aloe vera plants need more than just routine clipping; they also require specific attention. They need a lot of water and a fair deal of fertilizer, particularly in the summer when water evaporates more rapidly. To prevent the roots from becoming too moist, it is crucial to choose potted soil that drains properly. Root rot and other issues might result from using too much water.
Aloe vera plants typically only bloom once a year for two to three months, so it’s crucial to be aware of that. The flowers dry up and naturally wilt after this point. It is crucial to remove the dried flowers from the plant since they won’t re-grow and may attract pests or illnesses if they do.
Aloe vera plant blooming frequency might vary, however most established plants produce at least one raceme year. Some of these plants may even have many blooms during the growing season, extending the time you have to appreciate their beauty. However, it’s crucial to be aware that each plant might have a different level of bloom regularity.
To encourage greater blooming and general plant health, it is advisable to prune aloe vera plants after they have finished flowering. Proper trimming helps the plant maintain the desired shape and size, which keeps it looking attractive. This helps them make the most of the nutrients they have and helps them develop new leaves and “offsets.”
Keep in mind that aloe vera plants often need a few years to mature before they may begin to produce flowers. A plant’s ability to develop depends on its age and the amount of light it receives. Giving aloe vera plants the proper amount of sunlight is crucial for their overall growth and blooming potential since they need to be at least four years old before they are likely to put up a flower stalk.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that aloe vera plants planted inside have a lower likelihood of blooming than those grown outside in warm climates. It is a pretty wonderful thing if you are fortunate enough to have flowers on your aloe vera plant at home.
The Meaning and Blooming Process of Aloe Vera Flowers
Aloe vera plants often do not produce flowers until they are four years old or older. These flowers dangle in clusters and have vivid hues like orange, red, yellow, or pink. Their tubular form contributes to their distinctive charm. Once the flowers emerge, they often remain for a few weeks, improving the appearance of the plant.
Aloe vera plants develop flowers since it is the subsequent stage in their life cycle. It indicates that the aloe vera has developed enough to produce other plants. Because they attract flies, bees, and birds, the flowers are crucial for fertilization. These insects aid in the transfer of pollen from one flower’s male reproductive organs to another’s female reproductive organs. This enables breeding and ensures the production of seeds for the aloe vera plant’s subsequent generation.
An aloe vera plant in good condition may produce at least one raceme year and may even bloom twice or more throughout the growing season. The weather, the environment, and the plant itself may all have an impact on when and how frequently flowers bloom.
It’s crucial to be aware that aloe vera leaves only bloom for a little period, often 3 to 4 months. These lovely flowers typically bloom from late spring through summer, putting on a vibrant spectacle that draws both humans and bees. The aloe vera plant devotes all of its energy to producing flowers during this time, demonstrating its capacity for growth and the ability to produce further plants.
In several nations and among various populations, aloe vera leaves have various meanings. In general, flowers are often associated with romance, beauty, and love. For instance, the pink aloe vera flowers display these emotions while also demonstrating their tenacity. The vibrant hues of the flowers demonstrate the plant’s health and the role it plays in the intricate web of life in nature.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How long does it take for Aloe vera seeds to germinate? A: Aloe vera seeds typically take around 2 to 4 weeks to germinate under optimal conditions, including moist and warm soil.
Q: Can I grow Aloe vera indoors? A: Aloe vera can grow inside as long as it gets enough sunshine, ideally at least six hours of indirect sunlight each day. To avoid root rot, it’s also crucial to supply well-draining soil and water the plant sparingly.
Q: How often should I water my Aloe vera plant? Aloe vera plants, which are succulents, have evolved to withstand dry circumstances. It is better to fully water them just occasionally. Between waterings, let the soil fully dry out. Avoid overwatering since too much moisture might cause root rot.
Q: Does Aloe vera require any special care during the winter months? A: Aloe vera is a hardy plant, but it is sensitive to frost. If you live in a cold climate, it is advisable to bring your Aloe vera indoors or provide protection during freezing temperatures. Place it near a sunny window and reduce watering during the dormant period.
Q: How do I propagate Aloe vera plants? A: Plant pups or offsets that develop at the mother plant’s base are a method of propagating Aloe vera. Make sure the pup develops its own root system before carefully removing it from the parent plant and replanting it in a soil that drains properly. Aloe vera may also grow from leaf cuttings as an alternative.
Q: Can I use Aloe vera gel directly from the plant for skin care? A: Due to its soothing and moisturizing qualities, the gel from the Aloe vera plant is often utilized for a variety of skin care applications. Just split a leaf in half and scoop out the gel. Before using it on bigger regions, it’s best to do a patch test to look for any negative responses.
Q: Are there any health benefits associated with using Aloe vera internally? A: Aloe vera provides a number of advantages for internal health. Aloe vera may interact with certain drugs and have negative effects, so it’s vital to use caution and talk to a doctor before ingesting it internally.
Q: How long does an Aloe vera plant typically live? A: Depending on the growth environment, an Aloe vera plant’s lifespan might vary. Aloe vera plants survive for five to twenty-five years on average, but they may live much longer with the right care.
Q: Can I grow Aloe vera in a container or pot? A: Aloe vera may be planted in pots or containers, which gives growers more control over the growth process. Use well-draining soil, make sure the container has drainage holes, and pick a pot with adequate room for the plant’s growth.
Q: Is Aloe vera safe for pets? A: Aloe vera is well-known for its wide range of health benefits, but cats and dogs should avoid ingesting the plant’s gel or sap because of this risk. It is best to either use pet-friendly substitutes for indoor greenery or keep Aloe Vera plants out of reach of animals.
In the end, Aloe vera flowers eventually go through three stages: stage I is when they are young, stage II is when they are mature with closed buds, and stage III is when they are mature with open buds. Although the precise season might vary, the plant typically blooms once each year, beginning in early spring and lasting through summer. Before they can reach maturity and produce flowers, Aloe Vera plants must develop for a few years.
