Pruning hazelnut orchards is essential for promoting consistent yields. Proper pruning enhances tree health, encourages better air circulation, and allows sunlight to reach all parts of the tree. These practices lead to increased nut production and improved overall quality.
Hazelnut orchards require specific care to thrive and produce high-quality nuts. One of the most vital aspects of orchard management is pruning. This process involves selectively removing certain branches and shoots to shape the tree, enhance its growth, and optimize nut production. Effective pruning practices can lead to a healthier orchard and significantly impact yield consistency over time.

Understanding the unique growth habits of hazelnut trees is crucial for effective pruning. Hazelnuts are typically bushy in nature, with multiple stems emerging from the base. This growth habit necessitates thoughtful pruning strategies to ensure that each tree can produce an ample supply of nuts. Pruning not only helps with yield but also plays a key role in pest and disease management.
Importance of Pruning in Hazelnut Orchards
The importance of pruning in hazelnut orchards cannot be overstated. Regular pruning contributes to several key benefits:
- Improved Air Circulation: Pruning opens up the canopy, allowing for better airflow. This reduces humidity levels and minimizes the risk of fungal diseases.
- Enhanced Sunlight Penetration: Removing excess branches ensures that sunlight reaches all parts of the tree, promoting photosynthesis and healthier growth.
- Increased Yield: Properly pruned trees can produce higher yields due to improved flower and nut development.
- Better Tree Structure: Maintaining a well-structured tree helps support heavy nut loads without risking branch breakage.
Research has shown that the right pruning techniques can enhance not just the quantity but also the quality of hazelnuts produced. Well-pruned orchards tend to have larger nuts with better flavor profiles, making them more marketable. Understanding the optimal times and techniques for pruning is essential for any hazelnut grower.
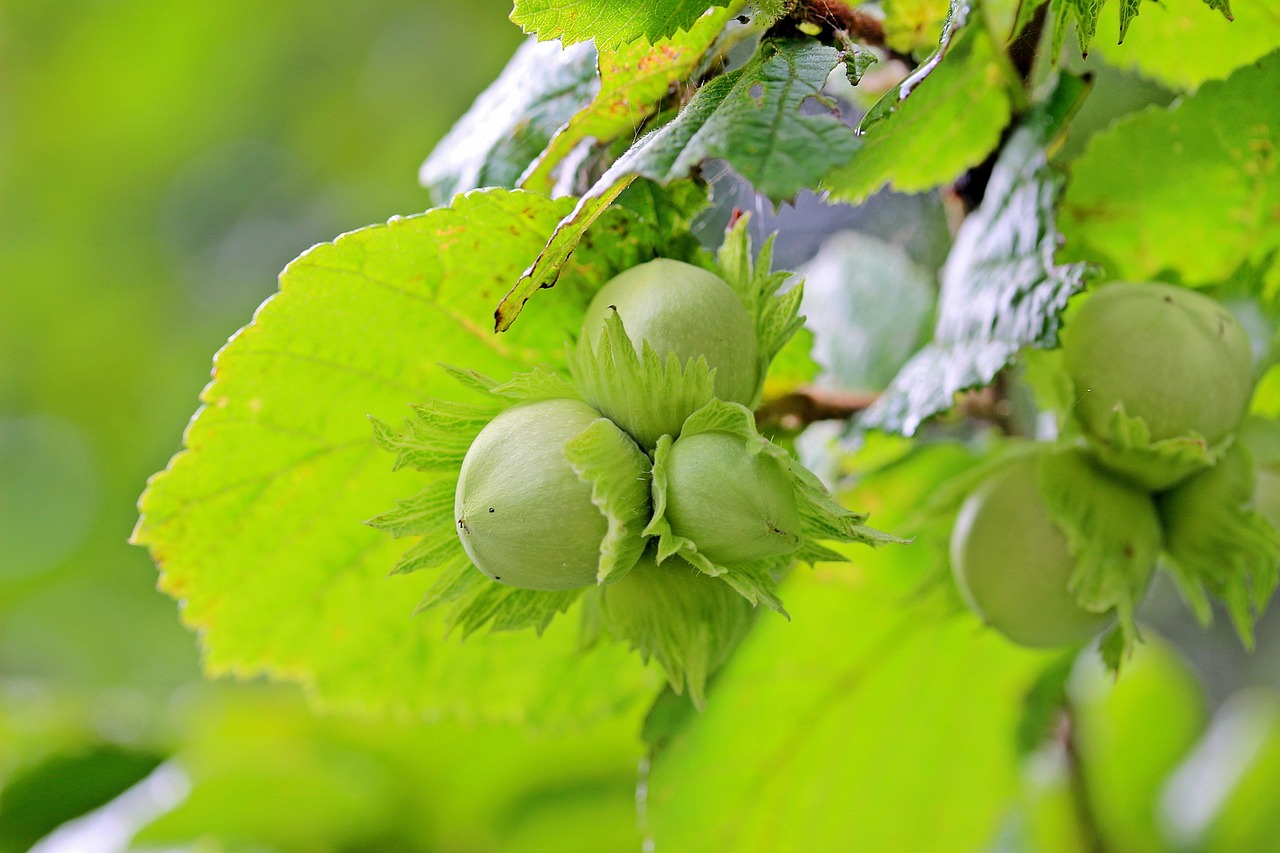

Key Pruning Techniques
There are several techniques that growers can employ when pruning hazelnut trees. Each method serves a specific purpose and can be adjusted based on the age and condition of the trees.
1. Thinning
This technique involves selectively removing branches to create space within the canopy. Thinning helps improve airflow and light penetration. It is best performed during the dormant season when the trees are not actively growing.
2. Heading Back
Heading back involves cutting back the tips of branches to encourage bushier growth. This method is especially useful for young trees, as it promotes branching and helps establish a strong framework for future growth.

3. Renewal Pruning
Renewal pruning focuses on removing older stems to encourage new growth from the base. This technique is crucial for maintaining productivity in mature orchards, as older stems tend to produce fewer nuts.
Ideal Timing for Pruning
The timing of pruning is critical for maximizing its effectiveness. Generally, hazelnut trees should be pruned during their dormant phase, which typically occurs in late winter to early spring before new growth begins. This timing helps reduce stress on the trees and minimizes the risk of damage from cold weather.
However, certain pruning techniques may be adapted based on specific conditions or goals. For example, heading back young trees can also be done in summer to control growth patterns more actively.
| Pruning Technique | Best Time for Pruning | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Thinning | Dormant season (late winter to early spring) | Improve airflow and light penetration |
| Heading Back | Dormant season or summer | Encourage bushier growth in young trees |
| Renewal Pruning | Dormant season (late winter to early spring) | Maintain productivity in mature orchards |
By understanding these techniques and their timing, orchardists can develop a comprehensive pruning strategy tailored to their specific needs. This proactive approach will lead to healthier trees and consistently high yields over the years.
Common Mistakes in Hazelnut Pruning
While pruning is essential for maintaining healthy hazelnut orchards, there are several common mistakes that growers should avoid. Understanding these pitfalls can help ensure that the pruning process yields the best results.
1. Pruning at the Wrong Time
One of the most significant mistakes is pruning at the wrong time. As mentioned earlier, pruning during the dormant season is crucial. Pruning too late in the spring can harm new buds and reduce yield. Additionally, pruning in the fall can expose cuts to cold temperatures, leading to damage and disease.
2. Over-Pruning
Another common mistake is over-pruning. Removing too many branches can stress the tree and reduce its ability to produce nuts. It’s essential to maintain a balance between removing excess growth and retaining enough foliage to support healthy growth and yield.
3. Neglecting Tree Structure
Failing to consider the natural growth habit of hazelnut trees can lead to poor structure. Growers should focus on creating an open canopy while maintaining a strong framework. This helps support the weight of nuts and enhances airflow.
Signs of Overgrown Hazelnut Trees
Recognizing when hazelnut trees have become overgrown is critical for effective management. Here are some signs that indicate it may be time for pruning:
- Dense Canopy: If the canopy is too dense, it limits light penetration, resulting in poor nut development.
- Long Branches: Branches that extend beyond the desired height can create challenges during harvesting and make the tree susceptible to wind damage.
- Poor Air Circulation: A lack of airflow can lead to increased humidity and a higher risk of fungal diseases.
- Dead or Diseased Wood: Any visible signs of dead or diseased branches should be addressed promptly to prevent spreading.
The Role of Tools in Pruning Hazelnut Orchards
The right tools are essential for effective pruning. Using appropriate equipment not only makes the job easier but also minimizes damage to the trees. Here are common tools used in hazelnut orchard pruning:
1. Hand Pruners
Hand pruners are ideal for small branches and precise cuts. They are useful for making clean cuts on younger trees during thinning and heading back.
2. Loppers
Loppers are designed for cutting larger branches. They provide more leverage than hand pruners, making them suitable for thicker branches that require more force.
3. Pruning Saws
For very large branches, a pruning saw is necessary. It allows for effective cutting without damaging the surrounding tissue of the tree.
4. Pole Saw
A pole saw is useful for reaching high branches without needing a ladder. This tool helps maintain safety while ensuring that taller parts of the tree are properly pruned.
Post-Pruning Care for Hazelnut Trees
After pruning, it’s essential to provide proper care to support recovery and encourage healthy growth. Here are some post-pruning care tips:
- Assess Tree Health: Check trees for any signs of disease or pests after pruning.
- Apply Fertilizer: A balanced fertilizer can provide nutrients that support new growth. Ensure it is appropriate for hazelnut trees and follow application guidelines.
- Irrigation: Adequate water is vital, especially during dry spells following pruning. Ensure that trees receive consistent moisture without overwatering.
- Pest Control: Monitor for pests that may be attracted to freshly cut wood and take necessary measures to prevent infestations.
The Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in how and when to prune hazelnut trees. Understanding these factors can help growers make informed decisions regarding their pruning practices.
1. Climate Conditions
The local climate conditions can affect tree growth patterns and health. In regions with milder winters, trees may emerge from dormancy earlier, necessitating adjustments in pruning timing.
2. Soil Quality
Soil quality impacts tree vigor and growth rates. Healthy, nutrient-rich soil will support better growth and may require different pruning practices compared to trees in poor soil conditions.
3. Water Availability
Adequate water availability is crucial for tree health. Trees under stress from drought may require different management strategies, including more careful pruning to maintain health.
By recognizing these environmental factors, growers can tailor their pruning strategies to enhance tree health and improve overall yields in their hazelnut orchards.
Pruning Hazelnut Trees for Quality and Yield
In addition to promoting consistent yields, pruning hazelnut trees is crucial for enhancing the quality of the nuts produced. The way trees are pruned can directly influence the size, taste, and overall marketability of the nuts. This section will explore best practices for pruning that focuses on both quality and yield.
Factors Influencing Nut Quality
Several factors contribute to nut quality, and pruning plays a significant role. Understanding these factors can help growers make better decisions regarding their pruning practices.
- Tree Age: The age of the tree affects its nut production. Younger trees may require different pruning techniques compared to mature ones.
- Light Exposure: Adequate light exposure is essential for photosynthesis. Pruning should ensure that light reaches all parts of the tree.
- Fruit Load Management: Balancing the number of nuts produced with the tree’s ability to support them is key. Overloading a tree can lead to smaller nuts.
- Pest and Disease Management: Healthy trees produce better quality nuts. Pruning can help reduce disease pressure and improve overall tree health.
Best Pruning Practices for Optimal Nut Quality
To maximize both the yield and quality of hazelnuts, certain best practices should be followed during the pruning process. These practices take into account the unique characteristics of hazelnut trees.
1. Balanced Canopy Management
A well-balanced canopy allows for optimal light penetration and air circulation. This can be achieved through strategic thinning and heading back. It is important to maintain an open canopy while ensuring that structural integrity remains intact. A balanced canopy will result in larger, better-quality nuts.
2. Selective Removal of Fruit Spurs
Fruit spurs are short lateral branches that bear nuts. Over time, these spurs can become less productive. Selectively removing older, less productive spurs while retaining younger ones can help ensure higher quality nut production. This practice encourages new growth and enhances overall productivity.
3. Maintaining Tree Height
Controlling the height of hazelnut trees can facilitate easier harvesting and improve nut quality. Taller trees may be harder to manage and can lead to uneven light distribution. Regular canopy management through pruning can help maintain a manageable height while ensuring that the tree remains healthy.
The Role of Training in Pruning Hazelnut Orchards
Training young hazelnut trees is another important aspect of orchard management that complements pruning. Proper training establishes a strong framework that supports future growth and nut production.
1. Establishing a Strong Framework
When young trees are trained correctly, they develop a robust structure that can support heavy nut loads. This involves selecting a main leader and allowing side branches to grow at appropriate angles. Training should begin early in the life of the tree to establish this framework effectively.
2. Importance of Early Intervention
Intervening early in a tree’s life through training can prevent future structural issues. Growers should regularly assess young trees and make adjustments as necessary to guide their development. Early intervention helps maintain a strong structure throughout the tree’s life.
Seasonal Considerations for Pruning
The timing of pruning is critical not only for tree health but also for ensuring high-quality nut production. Different seasons may call for different approaches:
1. Winter Pruning
Winter is often considered the best time for major pruning activities. Trees are dormant, making it easier to see their structure without foliage obstructing visibility. Winter pruning allows for significant changes without stressing the tree.
2. Summer Pruning
Summer pruning can be beneficial for managing tree size and encouraging new growth. This technique can be particularly effective for young trees that need shaping. However, care must be taken not to remove too much foliage, which could hinder photosynthesis.
Assessing Results After Pruning
After completing pruning, it is essential to assess the results to ensure that desired outcomes have been achieved. Observing how trees respond after pruning can provide valuable insights for future management decisions.
- Monitor Growth Patterns: After pruning, keep an eye on how new growth develops. Healthy new shoots indicate successful pruning.
- Evaluate Nut Size: During harvest time, evaluate the size and quality of nuts produced compared to previous years. This evaluation helps assess the effectiveness of pruning practices.
- Pest and Disease Presence: Check for any signs of pests or diseases post-pruning. A healthy tree will show fewer problems.
By continuously monitoring results and making adjustments as necessary, growers can refine their pruning strategies over time. This ongoing evaluation ensures that both yield and quality remain consistently high in hazelnut orchards.
Enhancing Hazelnut Orchard Management
In addition to pruning, other management practices can significantly impact the health and productivity of hazelnut orchards. Implementing a holistic approach that includes integrated pest management, soil health maintenance, and proper irrigation can further enhance yields and nut quality.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Utilizing an integrated pest management strategy is vital for maintaining the overall health of hazelnut trees. IPM combines various management practices to minimize pest impacts while reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. Here are some key components of IPM:
- Regular Monitoring: Conducting frequent inspections of trees helps identify pest populations early, allowing for timely interventions.
- Biological Control: Introducing natural predators of common pests can help keep populations in check without harming the environment.
- Cultural Practices: Implementing good cultural practices, such as crop rotation and maintaining tree vigor through proper irrigation and fertilization, can reduce pest pressures.
- Targeted Treatments: If chemical treatments are necessary, using targeted applications at the right time minimizes harm to beneficial organisms.
Soil Health Maintenance
The health of the soil directly influences tree growth and nut production. Healthy soils promote robust root systems and nutrient uptake. Here are some practices to maintain soil health:
- Regular Soil Testing: Conducting soil tests helps determine nutrient levels and pH, guiding fertilization practices.
- Organic Matter Addition: Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or mulch, improves soil structure and enhances water retention.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops during the off-season helps prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and add nutrients back into the soil.
Efficient Irrigation Practices
Proper irrigation is crucial for healthy hazelnut trees, especially during critical growth periods. Implementing efficient irrigation practices can conserve water and ensure that trees receive adequate moisture:
- Drip Irrigation: This method delivers water directly to the root zone, reducing waste and minimizing evaporation.
- Scheduling Irrigation: Monitoring soil moisture levels helps determine when to irrigate. Timing should align with the tree’s growth stages for optimal results.
- Mulching: Applying mulch around the base of trees helps retain soil moisture and suppress weeds, which can compete for water.
Final Thoughts
Pruning is a fundamental practice for achieving consistent yields in hazelnut orchards. By employing strategic pruning techniques tailored to the needs of individual trees and considering factors such as tree age, health, and environmental conditions, growers can significantly enhance both yield and nut quality.
Furthermore, integrating additional management practices like pest control, soil health maintenance, and efficient irrigation will create a synergistic effect that promotes the overall health of the orchard. This holistic approach not only ensures high-quality nut production but also contributes to sustainable farming practices that benefit the environment.
Ultimately, successful hazelnut orchard management requires ongoing education, observation, and adaptation. By continuously refining their techniques and responding to changing conditions, growers can cultivate thriving orchards that yield delicious nuts for years to come.
