Pruning hazelnut trees is essential for enhancing nut harvest efficiency. Proper pruning techniques improve tree structure, increase sunlight exposure, and promote air circulation, all of which contribute to higher yields and healthier trees.
Hazelnut trees, scientifically known as Corylus avellana, are a popular choice among nut growers due to their delicious nuts and versatility in various culinary uses. These trees can thrive in a range of climates and soil types, making them accessible to many farmers and gardeners. However, to maximize nut production, effective pruning practices are necessary.

Pruning is the process of selectively removing certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots. For hazelnut trees, pruning not only shapes the tree but also enhances its overall health and productivity. Regular maintenance through pruning helps to control the size of the tree, which is particularly important for harvesting purposes.
Benefits of Pruning Hazelnut Trees
There are several advantages to pruning hazelnut trees that directly impact harvest efficiency:
- Improved Sunlight Exposure: Pruning opens up the canopy, allowing sunlight to reach more branches and leaves. This exposure is crucial for photosynthesis and ultimately leads to better nut development.
- Enhanced Air Circulation: Properly pruned trees have better airflow. Good circulation reduces the risk of fungal diseases that can affect nut yield.
- Increased Yield: By removing dead or overcrowded branches, nutrients can be distributed more effectively, resulting in a higher nut yield.
- Ease of Harvesting: A well-pruned tree is easier to access during harvest time. This efficiency can save time and labor costs.
Understanding the growth cycle of hazelnut trees is essential for effective pruning. Typically, these trees bear fruit on new growth from the previous year. Therefore, knowing when and how to prune is critical for maximizing next season’s harvest.

Key Pruning Techniques
There are several key techniques employed when pruning hazelnut trees:
- Thinning: This involves removing entire branches back to their origin. Thinning reduces overcrowding, allowing remaining branches to grow more vigorously.
- Head Training: This technique encourages a specific height for the trees. By cutting the main leader branch back, lateral branches develop more fully.
- Renewal Pruning: This method focuses on cutting older branches to stimulate the growth of new shoots. It helps maintain a mix of old and young wood.
The timing of pruning also plays a significant role in its effectiveness. Generally, pruning should occur during the dormant season, usually late winter or early spring, before buds begin to swell. This timing minimizes stress on the tree and helps prevent sap loss.
Pruning Tools and Safety
Using the right tools is essential for effective and safe pruning. The following tools are commonly used:
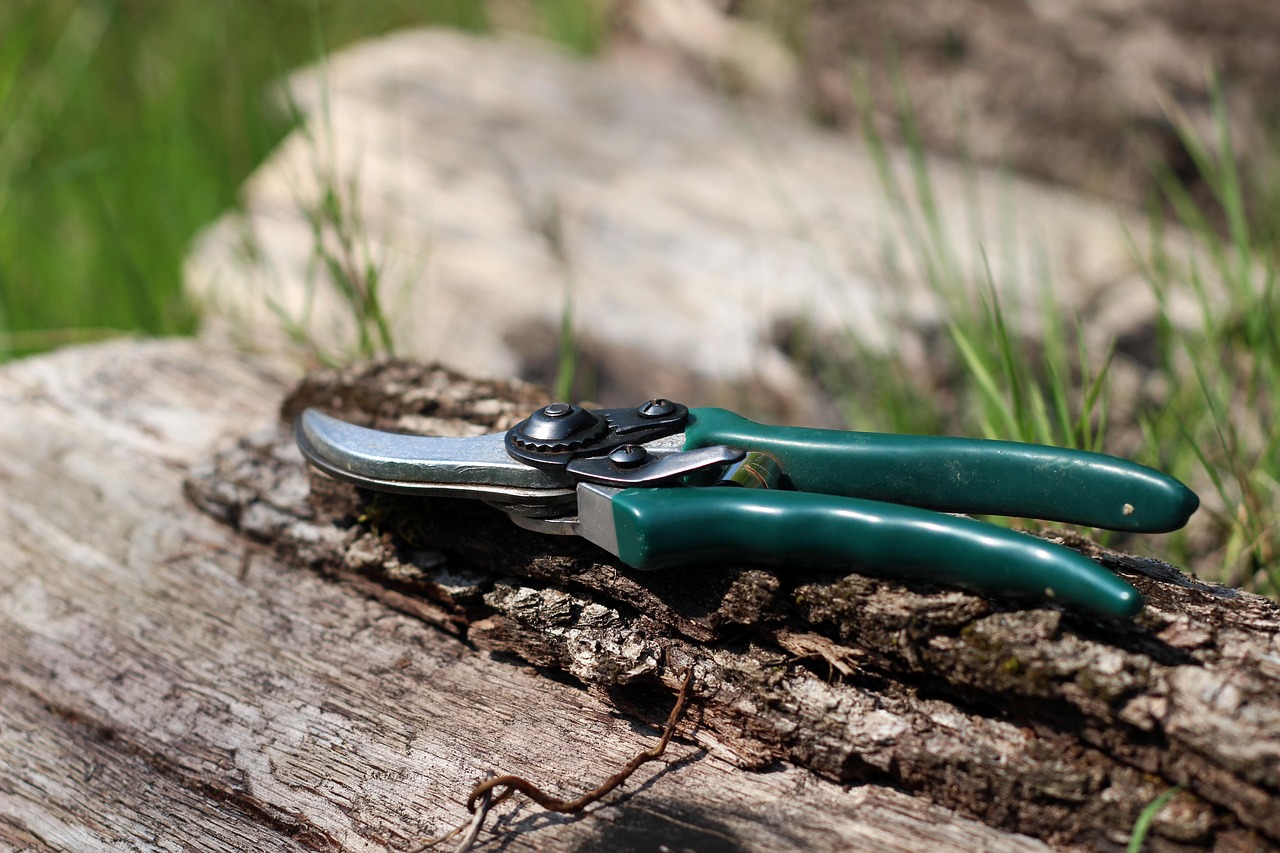

| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Hand Pruners | Ideal for cutting small branches and shoots. |
| Loppers | Used for thicker branches that require more leverage. |
| Saw | Necessary for larger branches that cannot be cut with pruners or loppers. |
| Safety Gear | Includes gloves and goggles to protect from cuts and debris. |
Ensuring that tools are sharp and clean is vital. This practice prevents damage to the tree and reduces the risk of spreading diseases between plants.
In summary, effective pruning is a critical component in managing hazelnut trees for optimal nut harvest efficiency. By understanding the benefits of pruning, employing key techniques, utilizing appropriate tools, and ensuring safety, growers can significantly enhance their yields and maintain the health of their trees.
Understanding Hazelnut Tree Growth Patterns
To effectively prune hazelnut trees, it is essential to understand their growth patterns. These trees typically exhibit vigorous growth, and knowing how they develop can guide pruning decisions. Hazelnut trees can grow up to 20 feet tall and often feature a bushy habit. Their growth is characterized by the following:
- Canopy Structure: Hazelnut trees have a multi-stemmed structure. Each stem can produce numerous branches, which need careful management through pruning.
- Branch Development: New growth emerges from buds located on previous year’s wood. This means pruning should focus on shaping these branches for optimal fruit production.
- Root System: A healthy root system supports robust growth. Pruning should not interfere with root development, so care must be taken not to disturb the roots excessively.
Understanding these aspects helps growers make informed decisions about when and how to prune their trees, ensuring better nut yields in the long run.
Seasonal Pruning Considerations
The timing of pruning is crucial for the health and productivity of hazelnut trees. Different seasons present unique opportunities and challenges:
Winter Dormancy
Pruning during winter dormancy is the most common practice. At this time, trees are less susceptible to disease, and sap loss is minimized. Key points to remember include:
- Timing: Aim to prune between late winter and early spring, just before bud break. This timing allows trees to heal quickly as they enter their growing phase.
- Focus on Structure: Use this period to shape the tree, removing any dead or damaged branches and creating an open canopy.
Summer Pruning
Summer pruning can also be beneficial, particularly for controlling the size of the tree and managing excessive growth. Important considerations include:
- Light Management: Pruning in summer allows for better sunlight penetration, which can enhance nut development.
- Removal of Suckers: This is an excellent time to remove suckers or water sprouts that can compete with fruiting branches for nutrients.
Common Mistakes in Pruning Hazelnut Trees
Even experienced growers can make mistakes while pruning. Being aware of common pitfalls can help improve practices:
- Over-Pruning: Removing too many branches can stress the tree and reduce yields. Always aim for balance.
- Poor Timing: Pruning at the wrong time can lead to sap loss or increased susceptibility to disease.
- Ignoring Tree Health: Always assess the overall health of the tree before pruning. Weak or diseased trees may require different approaches.
Post-Pruning Care
After pruning, it’s important to provide proper care to ensure the health of the tree and its ability to produce nuts effectively. Some best practices include:
- Watering: Ensure that trees receive adequate water, especially following pruning, as they may experience stress during recovery.
- Nutrient Management: Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring to support new growth and nut development.
- Disease Monitoring: Keep an eye out for signs of disease or pest infestations after pruning, as open cuts can attract pests.
Evaluating Pruning Results
Once the growing season progresses, evaluating the results of pruning is essential for future planning. Consider these factors when assessing your trees:
- Nut Production: Compare the yield of harvested nuts against previous years to determine if your pruning practices were effective.
- Tree Health: Monitor the overall vitality of the tree. Healthy new growth indicates successful pruning.
- Pest Presence: Check for any increased pest activity or disease presence that may have resulted from pruning practices.
This evaluation process will help refine your techniques and improve overall harvest efficiency in subsequent seasons.
Advanced Pruning Techniques
For growers looking to further enhance their skills, several advanced techniques can be explored:
- Coppicing: This technique involves cutting back a tree to ground level to promote vigorous new growth. Coppicing can rejuvenate older trees and improve nut production.
- Pollarding: Similar to coppicing but involves cutting branches back to a specific height. This method is less common but can be useful for managing tree height.
- Training Systems: Implementing training systems like central leader or open vase methods can help shape young trees for optimal fruiting habits.
These advanced techniques require careful planning and understanding of tree physiology but can lead to outstanding results in nut harvest efficiency.
Common Pests and Diseases Affecting Hazelnut Trees
Maintaining the health of hazelnut trees is crucial for achieving optimal nut harvest efficiency. Unfortunately, these trees can be susceptible to various pests and diseases that may hinder their growth and productivity. Understanding these threats allows growers to implement effective management strategies.
Common Pests
Several pests can pose a threat to hazelnut trees. Knowing how to identify and manage these pests is essential for protecting the crop:
- Filbert Worm: This caterpillar feeds on hazelnut leaves and nuts, causing significant damage. Signs include ragged foliage and eaten nuts. Controlling populations through monitoring and targeted insecticides can be effective.
- Spider Mites: These tiny pests can cause yellowing leaves and webbing on branches. Regularly inspecting for signs of infestation and applying miticides when needed can help in managing these pests.
- Leafrollers: These larvae roll leaves together to feed inside. Infestations can lead to reduced photosynthesis. Hand-picking or using biological controls may be effective methods for control.
Common Diseases
Diseases can significantly affect the health of hazelnut trees. Here are some common diseases to be aware of:
- Eastern Filbert Blight: This fungal disease is one of the most serious threats to hazelnut trees. It causes cankers, which can girdle branches and lead to tree death. Pruning out affected branches and applying fungicides can help manage this disease.
- Powdery Mildew: This fungal issue appears as a white coating on leaves and can inhibit growth. Ensuring proper air circulation through pruning and applying fungicides can help control its spread.
- Corylus Root Rot: Caused by soil pathogens, this disease affects the root system, leading to tree decline. Proper soil drainage and avoiding overwatering are key preventive measures.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
Implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies can provide a holistic approach to pest and disease control. Here are some effective components of an IPM plan:
- Monitoring: Regularly inspect trees for signs of pests and diseases. Early detection is key to successful management.
- Biological Control: Introduce natural predators of pests, such as ladybugs for aphids or nematodes for soil-borne pests, to reduce pest populations.
- Cultural Practices: Maintain healthy trees through proper watering, fertilizing, and pruning practices to bolster their resistance against pests and diseases.
- Chemical Control: Use pesticides or fungicides as a last resort. When necessary, select targeted products that minimize harm to beneficial insects.
The Role of Soil Health in Pruning Success
The health of the soil directly impacts the growth and productivity of hazelnut trees. Healthy soil promotes strong root systems, which are essential for nutrient uptake and overall tree vigor. Here are key aspects of maintaining soil health:
Soil Composition
A balanced soil composition is vital for sustaining hazelnut trees. Key components include:
- Nutrients: Essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are crucial for tree growth. Regular soil testing can identify nutrient deficiencies that may need addressing through fertilization.
- Organic Matter: Incorporating organic material, such as compost or mulch, improves soil structure, water retention, and microbial activity.
Soil pH Levels
The pH level of the soil affects nutrient availability. Hazelnut trees thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil, ideally between 6.0 and 7.0. Regular pH testing allows growers to make necessary adjustments through lime or sulfur applications:
| Soil pH Level | Nutrient Availability |
|---|---|
| Below 6.0 | Nutrient availability decreases; consider adding lime. |
| 6.0 – 7.0 | Optimal range for hazelnut trees; nutrients are readily available. |
| Above 7.0 | Nutrient availability may be limited; consider adding sulfur to lower pH. |
Irrigation Practices
Irrigation is another critical component in maintaining soil health and promoting effective pruning outcomes. Hazelnut trees require consistent moisture, particularly during dry spells. Proper irrigation practices include:
- Drip Irrigation: This method provides water directly to the root zone, minimizing waste and reducing the risk of fungal diseases associated with overhead watering.
- Watering Schedule: Establish a watering schedule based on soil moisture levels. Regular monitoring ensures that trees receive adequate moisture without overwatering.
By implementing these practices focused on soil health, irrigation, and pest management, growers can create an optimal environment for their hazelnut trees, leading to improved nut harvest efficiency.
Additional Considerations for Successful Pruning
In addition to the previously discussed practices, several other factors can enhance the effectiveness of pruning hazelnut trees. These considerations contribute to the overall health and productivity of the trees, ensuring that growers achieve the best possible yields.
Choosing the Right Varieties
Selecting appropriate hazelnut tree varieties can significantly influence pruning success and nut production. Different varieties may have varying growth habits, disease resistance, and yield potential. When choosing varieties, consider:
- Growth Habit: Some varieties naturally grow taller or bushier than others. Selecting a variety that aligns with your pruning goals can make maintenance easier.
- Disease Resistance: Opt for varieties known for their resilience to common pests and diseases. This choice can lead to healthier trees and a reduced need for intervention.
- Climate Adaptability: Ensure that the chosen variety is suitable for your local climate, as this will impact overall growth and fruiting.
Regular Assessment and Adaptation
Regular assessment of your hazelnut trees is essential in adapting pruning strategies over time. Factors such as growth rates, pest pressures, and weather conditions can change, necessitating a flexible approach to tree management. Conduct annual evaluations that include:
- Growth Analysis: Monitor tree growth patterns each season to determine if your pruning methods are effective. Adjust techniques based on observed results.
- Pest and Disease Monitoring: Keep detailed records of pest and disease occurrences to identify trends and develop targeted management strategies.
- Yield Tracking: Document nut yields annually to assess the impact of different pruning techniques and overall tree health.
Community Resources and Support
Engaging with local agricultural extensions, horticultural societies, or hazelnut growers’ associations can provide valuable support and resources. These organizations often offer workshops, field days, and educational materials that can enhance your understanding of hazelnut tree management. Benefits of community engagement include:
- Knowledge Sharing: Learning from experienced growers can provide insights into best practices and innovative techniques.
- Access to Research: Many agricultural institutions conduct research on pest management, soil health, and pruning techniques relevant to hazelnut cultivation.
- Networking Opportunities: Connecting with fellow growers can lead to partnerships and collaborative projects, fostering a supportive community.
Final Thoughts
Pruning hazelnut trees effectively is a multifaceted process that significantly impacts nut harvest efficiency. By understanding tree growth patterns, implementing appropriate techniques, and maintaining soil health, growers can maximize their yields while ensuring the long-term vitality of their trees.
Incorporating integrated pest management strategies further enhances tree health, allowing for a proactive approach to challenges that may arise. Regular evaluation of pruning practices, selection of suitable varieties, and engagement with community resources provide additional layers of support in successful hazelnut cultivation.
The journey of managing hazelnut trees is continuous. With proper techniques and a commitment to learning, growers can enjoy fruitful harvests and contribute to the sustainability of hazelnut production. Ultimately, investing time and effort into understanding the nuances of pruning will yield benefits for both the trees and the harvest for years to come.
