As a home gardener, I always refer to the hardiness zones for plants before choosing what to grow in my garden. Hardiness zones are determined based on the average annual minimum temperature, which helps us determine which plants will thrive in our specific climate.
Here’s how to use hardiness zones for your plants:
| Identify your location on the hardiness zone map. |
| Choose plants that are recommended for your zone. |
| Consider microclimates in your area that may impact your zone. |
| Be aware that hardiness zones are just guidelines and not perfect predictors of plant survival. |
By using hardiness zones, you can make informed decisions about what to grow in your home garden and increase your chances of a successful harvest.
Understanding Hardiness Zones
Everyone knows there are a variety of plants out there, but did you know that different plants have different hardiness zones? Hardiness zones help you to understand what plants are going to work best in your climate.
In this article, I’m going to share some information about hardiness zones and show you how you can use them to select the best plants for your garden.
What are Hardiness Zones?
As a passionate gardener, I know that understanding Hardiness Zones is crucial to choosing the right plants for your garden. Hardiness Zones are a geographical categorization of areas based on their minimum winter temperature. This system is used to help gardeners determine which plants are most likely to survive in a particular climate.
| Zone | Average Minimum Temperature (Fahrenheit) | Average Minimum Temperature (Celsius) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -60 | -51 |
| 13 | 60 | 16 |
Once you’ve determined the Hardiness Zone of your area, you can use this information to choose the right plants for your garden. Look for plants that have a Hardiness Zone range that includes your area’s zone. This way, you can ensure that your plants will survive the winter and thrive in your garden. Pro Tip: Always verify Hardiness Zone information on plant labels and online resources to get the most current data.
What Determines a Plant’s Hardiness Zone?
Understanding the hardiness zones is essential to decide what plants to grow in a particular area. These zones are determined by multiple climatic factors that affect the growth of plants.
The primary factors that determine a plant’s hardiness zone are:
| Temperature: | The average minimum temperature is a significant factor in determining the hardiness zone of an area. |
| Climate: | The amount and distribution of rainfall, humidity, and wind speeds affect the hardiness zone. |
| Altitude: | As altitude increases, temperature and air pressure decrease, making it difficult for some plants to thrive. |
| Latitude: | The position of an area on Earth’s surface determines the amount of sunlight received, impacting plant growth. |
Knowing the hardiness zone of your area will help you pick plants that are most likely to grow and survive, making gardening more successful.
Pro Tip: Check your hardiness zone before deciding what plants to grow, and make sure to choose plants that can thrive in your area’s climate.
Importance of Using Hardiness Zones
As someone who loves gardening, I have found that using hardiness zones is crucial for success. Hardiness zones, which categorize areas based on temperature and climate, are essential for choosing the right plants and ensure that they will thrive in their new environment.
By understanding hardiness zones, you can save time, effort, and money. Plants that are not adapted to your hardiness zone may require more care or have a higher chance of failure. Some plants may even turn into invasive species if they’re not suitable for your area.
To use hardiness zones, find out what zone you’re in using an online map or by consulting with your local gardening center. Once you know your hardiness zone, choose plants that are recommended for that zone.
Using hardiness zones may seem like common sense, but it is often overlooked by amateur gardeners. By selecting the right plants for your climate, you can ensure that your garden will thrive for years to come.
| Pro tip: |
|---|
| Don’t be afraid to experiment with different plant varieties, but make sure to research their climate requirements before planting. |
Finding Your Local Hardiness Zone
Gardening is an enjoyable and rewarding hobby, but the key to success is knowing what to grow and when. One important factor when deciding what plants to grow is your local hardiness zone. In this article, I’ll provide tips on how to use hardiness zones so you can make the most of your garden.
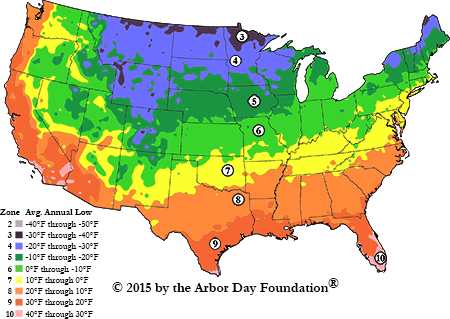
Locating USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
As a gardening enthusiast, I always make sure to check my USDA Plant Hardiness Zone before planting any seeds or choosing which plants to grow in my garden.
To find your local hardiness zone, simply go to the USDA website and search for their Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
Once you locate your zone, use it as a guide to determine which plants are best suited for your climate. For example, if you live in a colder zone, you may want to consider plants that can withstand frost or low temperatures. On the other hand, if you live in a warmer zone, you may want to choose plants that can thrive in hot and humid climates.
By using the hardiness zones to decide what to grow, you can make informed decisions that will help you achieve a thriving and beautiful garden. Pro Tip: Make sure to also consider factors such as soil type and light exposure when choosing your plants!
Using Zip Code to Determine Hardiness Zone
Using my zip code to determine my hardiness zone has helped me decide what to grow in my garden. By figuring out my hardiness zone, I can choose plants that are best suited for my local climate and weather conditions.
Here’s how you can determine your hardiness zone using your zip code:
| Look up a hardiness zone map online or visit your local gardening center to find one. |
| Enter your zip code into the map or search for it on the map to find out what zone you are in. |
| Choose plants that are labeled as suitable for your hardiness zone to ensure they will survive and thrive in your garden. |
This method has helped me to plan my gardening efforts better and achieve more successful yields.
Local Extension Service Resources
When it comes to gardening, knowing your local hardiness zone can make all the difference in your success. The good news is that finding your zone is easy with the help of your local extension service resources.
To find your zone, follow these steps:
| Visit the website of your local extension service and search for their hardiness zone map. |
| Enter your zip code to determine the zone for your specific location. |
Once you know your zone, you can use it to make informed decisions about what plants will thrive in your area. For instance, if you live in a warmer zone, you may have success growing citrus trees or succulents, while those in cooler zones may need to focus on frost-tolerant crops like kale or carrots.
Using the local extension service resources for finding your hardiness zone will help you make smart choices and ultimately have a more fruitful garden.
Choosing Plants Based on Hardiness Zones
When it comes to my garden, I want to make sure the flowers and vegetables I am growing are going to get the best possible chance of thriving in the local climate. To do this, I use the hardiness zones for plants. Hardiness zones provide me with a reliable way to determine which plants are best suited for growing in my area.
Let’s take a look at how hardiness zones can tell us what plants to grow in our garden.
Selecting Plants for Your Hardiness Zone
As a gardener, selecting plants for your hardiness zone can make all the difference in the success of your garden. Hardiness zones are based on the average minimum temperature of a region, indicating which plants are best suited for the area’s climate.
Here’s how I use hardiness zones for plants to decide what to grow in my garden:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Determine your hardiness zone using a map or online resource. |
| 2 | Select plants that are recommended for your zone, ensuring they can handle the minimum temperature. |
| 3 | Consider microclimates in your garden, such as areas that receive more sun or are highly sheltered. |
| 4 | Experiment with plants that are close to the borderline of your zone, but make sure to protect them during extreme weather. |
By selecting plants based on hardiness zones, you can set your garden up for success and enjoy healthy, thriving plants throughout the growing season.
Consideration of Microclimates
When selecting plants for my garden, I always take into consideration the microclimates present within my larger hardiness zone. Microclimates are small areas within a zone that have their own unique climate and weather patterns. By selecting plants that are well-suited for the specific microclimate in a given area of my garden, I can ensure optimal growth and health for my plants.
For example, I have noticed that one area of my garden gets more shade and moisture, while another area gets more sun and wind. To select plants that are best-suited for these areas, I consult a plant hardiness zone map and take note of the recommended plants for my zone, as well as each plant’s specific requirements for amount of sun, water, and wind exposure. This has helped me make informed choices about what to grow, which ultimately leads to healthier plants and a more successful garden.
Pro Tip: Before planting, observe your garden’s microclimates and do some research to find plants that are best-suited for those specific conditions.
Flexibility with Different Zones
As a gardener, I am always looking for ways to make my plant choices more efficient and tailor them to suit my local climate. Using hardiness zones is the best way to achieve this, as it helps me select plants that can grow successfully in my area without wasting time or resources.
Different zones have different climates, which means that not all plants can survive in all zones. By checking my zone on a hardiness zone map, I can choose plants with a better chance of growth success by selecting plants that can withstand local temperatures and temperature fluctuations.
The flexibility that comes with hardiness zones means that I can bring a variety of plants into my garden, as long as they are suited to my zone’s climate, which makes my garden look and feel more diverse.
Not only does this save me money on failed plants, but it also allows me to focus on growing plants that will thrive in my locality, resulting in a more successful and satisfactory gardening experience.
Caring for Your Plants in a Specific Zone
As a home gardener, it’s important to understand your geographical location and its associated hardiness zone. Knowing your hardiness zone is the key to successfully growing the right plants in your garden. By understanding the zones and their corresponding temperature ranges, you can easily decide what plants to grow and how to care for them.
Let’s explore the specifics of hardiness zones and how to use them for your gardening success.
Understanding Climate Factors
As a gardener, understanding the climate factors that impact your plants’ health is critical to their survival. The USDA Hardiness Zone map is a valuable tool that can aid in selecting plants that can withstand the climate stressors characteristic of your zone.
Here are some key climate factors to consider:
| Temperature: | Plants require a specific range of temperatures to grow optimally. Assess the average temperature range of your zone to ensure that the plants you select can thrive in that climate. |
| Precipitation: | Water is a crucial component of plant growth, and plants require different ranges of water depending on their species. Look for plants that require the same amount of water as provided by the natural precipitation cycles in your zone. |
| Soil: | The composition of soil in each zone can vary greatly, affecting the nutrient profile available to plants. Check for soil acidity, alkalinity, and texture information when selecting plants. |
| Light: | Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis and plant growth. Identify areas of sun and shade in your garden and select plants that can tolerate the light conditions of your zone. |
By using the USDA Hardiness Zone map to get an understanding of the climate factors in your specific zone and then selecting suitable plants can make all the difference to a successful garden.
Applying Best Practices for Your Hardiness Zone
Living in the Northeastern United States, where the weather can be unpredictable and consistently cold in the winter, I have found it imperative to use hardiness zones for plants to decide what to grow and how best to cultivate them.
Hardiness zones are geographic regions that provide essential information about the climatic conditions of a particular place, including the average minimum temperature during the winter. Using these zones, you can determine which plants are most likely to thrive in your area and which ones may struggle to survive.
For example, in zone 5, where I live, fruits like apples and peaches thrive, while tropical plants like plumeria and hibiscus may struggle. On the other hand, certain vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and kale can withstand the winters and provide a robust harvest.
In summary, by applying best practices for your hardiness zone, you can choose the right plants for your climate and grow them successfully, ensuring a bountiful garden that thrives in every season.
Being Prepared for Unexpected Weather Events
Living in an area prone to unexpected weather events can pose a significant threat to your plants. As someone living in hardiness zone 7a, I have found that the following tips have helped me prepare and care for my plants during such events.
| 1. Research plants that can withstand extreme weather in your specific hardiness zone. Hardiness zones map out regions based on the plant’s ability to withstand frost and low temperatures. I have found this useful in deciding what plants to grow. |
| 2. Protect your plants before the event occurs. Some typical ways include adding a layer of mulch or providing a temporary cover over them. |
| 3. Keep an eye out for signs of stress in your plants, such as burnt leaves or rotting. Be sure to remove any diseased or dead sections of the plant to prevent further damage. |
| 4. Have a plan in place for how to restore your garden once the event has passed. This may include replanting, fertilization, or soil testing. |
By taking the time to prepare and care for your plants, you can navigate unexpected weather events and keep your garden thriving.
