Lettuce growth stages include seed germination, seedling establishment, vegetative growth, and flowering/seed production. In the initial stage, lettuce seeds germinate and develop into seedlings.
As they mature, they progress to the vegetative growth stage, where leafy growth occurs. Finally, the plants enter the flowering/seed production stage, signaling the end of their life cycle before harvest. Lettuce, scientifically known as lactuca sativa, is a versatile and nutritious leafy green vegetable widely consumed across the globe.
From its humble beginnings as small seeds, lettuce goes through distinct growth stages until it reaches maturity. Understanding these growth stages is essential for successful cultivation and maximizing crop yield. This article explores the various phases of lettuce growth, from seed germination to flowering and seed production, providing valuable insights for both novice and experienced growers. Read on to discover the fascinating journey of lettuce from a tiny seed to a luscious, vibrant plant ready for harvest.
Understanding The Growth Cycle
Germination Stage
The germination stage is the beginning of the lettuce growth cycle. During this stage, the lettuce seeds absorb water and swell, initiating the process of germination. Here’s what happens during the germination stage:
- Seeds are planted in soil or a growing medium.
- Adequate moisture and temperature conditions are required for germination to occur.
- The seed coat breaks open, and a root emerges, followed by the shoot.
- The root anchors the seedling and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
- The shoot grows towards the surface, pushing through the soil.

As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Table of Contents
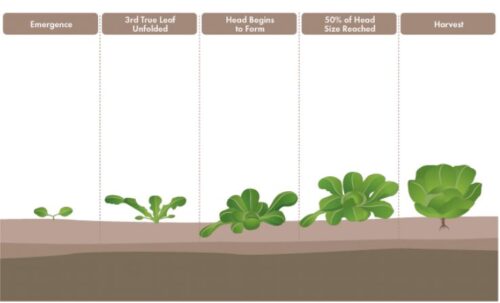
Seedling Stage
After successful germination, the lettuce enters the seedling stage. In this stage, the young plant develops its first set of true leaves and establishes a stronger root system. Here’s what you need to know about the seedling stage:
- The cotyledons, or seed leaves, become visible as they emerge from the soil.
- The first true leaves develop and start resembling the mature lettuce leaves.
- The root system expands as more roots develop, aiding in nutrient and moisture absorption.
- The seedling requires proper care, including adequate sunlight, water, and protection from pests or harsh weather conditions.
- The seedling stage is crucial for the lettuce’s future growth and overall health.
Vegetative Stage
The vegetative stage is a period of rapid growth and leaf production in the lettuce plant. During this stage, the plant focuses on leaf development rather than flower and seed production. Here’s what happens during the vegetative stage:
- The lettuce plant continues to develop more leaves, forming a dense rosette-like structure.
- The root system expands further, absorbing nutrients from the soil to support the fast growth.
- The plant requires ample sunlight, water, and nutrients to thrive.
- Pruning or thinning may be necessary to prevent overcrowding and promote better air circulation.
- The vegetative stage is crucial for establishing a healthy foundation for a productive harvest.
Remember, understanding the growth cycle of lettuce plants, from germination to the vegetative stage, is essential for successful cultivation. By providing the necessary care and meeting the specific needs of each stage, you can ensure optimal growth and a bountiful lettuce harvest.
Factors Affecting Lettuce Growth
Lettuce, a leafy green vegetable, goes through several growth stages before it reaches maturity. Understanding the factors that influence lettuce growth is essential for successful cultivation. Here, we explore three primary factors – light requirements, temperature and climatic conditions, and soil health and fertility – that significantly impact the growth of lettuce.
Light Requirements:
- Lettuce plants thrive in direct sunlight, requiring at least 6-8 hours of full sun exposure daily.
- Insufficient light can result in slow growth and smaller, less flavorful lettuce leaves.
- Adequate sunlight ensures optimal photosynthesis and the production of chlorophyll, crucial for leaf development and vibrant coloration.
- Inadequate light can lead to elongated and spindly lettuce plants as they stretch towards the light source.
Temperature And Climatic Conditions:
- Lettuce is a cool-season crop, preferring moderate temperatures between 45°f and 75°f (7°c and 24°c).
- Extreme heat can cause lettuce to bolt, where the plant rapidly produces a flowering stem, resulting in bitter-tasting leaves and overall stunted growth.
- Similarly, prolonged exposure to frost or freezing temperatures can damage lettuce seedlings, inhibiting growth and leading to wilting or death.
- Consistent temperature fluctuations can negatively affect lettuce growth, so it’s crucial to provide a stable climate for optimal development.
Soil Health And Fertility:
- Well-draining soil enriched with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, promotes healthy lettuce growth.
- A ph level between 6.0 and 7.0 is ideal for lettuce cultivation, ensuring nutrient availability and absorption.
- Adequate soil moisture is crucial for lettuce growth, as water deficiencies can result in stunted plants or bitter-tasting leaves.
- Adding nitrogen-rich fertilizers can encourage leaf development, while potassium promotes root growth and overall plant vigor.
- Maintaining proper soil fertility through regular amendments and soil testing ensures optimal conditions for robust lettuce growth.
Understanding and effectively managing these factors will help you cultivate thriving lettuce plants. Providing adequate light exposure, maintaining suitable temperature and climatic conditions, and ensuring soil health and fertility are key to achieving bountiful and flavorful lettuce harvests.
Germination Stage
Lettuce Growth Stages: Germination Stage
Lettuce is a popular leafy vegetable that goes through several growth stages before it’s ready for harvesting. The germination stage is the first crucial step in lettuce growth, where the seeds sprout and develop into small seedlings. In this section, we will explore the seed selection and preparation process, as well as the optimal planting conditions, and the timeline and requirements for successful lettuce germination.
Seed Selection And Preparation:
- Choose high-quality lettuce seeds from reputable suppliers to ensure the best germination rates.
- Prior to planting, it’s important to perform a seed viability test to ensure that the seeds are viable and will germinate successfully.
- Check the seed packet for the recommended planting depth and spacing for the specific lettuce variety you are growing.
- Consider treating the seeds with a seed primer or a germination enhancer to improve the germination process.
Optimal Planting Conditions:
- Lettuce seeds require a cool and moist environment to germinate effectively.
- The ideal temperature for lettuce germination ranges between 45°f (7°c) and 75°f (24°c).
- Provide adequate sunlight or artificial light to promote germination. Ensure the seeds receive at least 12 hours of light per day.
- Maintain consistent moisture levels in the soil by watering regularly, but avoid overwatering, as it can lead to rotting of the seeds.
Germination Timeline And Requirements:
- Lettuce seeds typically germinate within 7 to 14 days, depending on the variety and environmental conditions.
- The seeds require a constant soil temperature between 50°f (10°c) and 70°f (21°c) to germinate successfully.
- Ensure a well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter to provide the necessary nutrients for seedling growth.
- Adequate air circulation is crucial for preventing diseases and ensuring healthy germination. Consider using a small fan in the germination area to promote air movement.
With careful seed selection and preparation, along with the provision of optimal planting conditions, you can create the ideal environment for lettuce germination. Following the recommended timelines and requirements will allow your lettuce seeds to sprout into healthy seedlings, setting the stage for further growth and development in the lettuce growth cycle.

Seedling Stage
Transplanting Seedlings
Transplanting seedlings is a crucial step in ensuring the successful growth of lettuce. Here’s what you need to know:
- Seedlings should be transplanted into the ground or a container when they have developed their first true leaves, typically 2-3 weeks after germination.
- Choose a location that provides adequate sunlight and well-drained soil for optimal growth.
- Prior to transplanting, make sure to water the seedlings thoroughly to ensure their roots are well-hydrated.
- Create holes in the soil or container that are slightly larger than the root ball of the seedlings.
- Carefully lift the seedlings by their leaves or root ball, being cautious not to damage the fragile roots.
- Place the seedlings into the prepared holes, ensuring that the root ball is covered with soil.
- Gently press the soil around the seedlings to secure them in place.
- Water the transplanted seedlings immediately after planting to help them establish and reduce transplant shock.
Essential Care Practices
To promote healthy growth during the seedling stage, following these essential care practices is vital:
- Provide consistent moisture by watering the seedlings regularly, keeping the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged.
- Mulch around the base of the seedlings to retain soil moisture and prevent weed growth.
- In case of extreme heat or direct sunlight, consider providing shade or using row covers to protect the seedlings.
- Apply a balanced liquid fertilizer every two weeks to provide necessary nutrients for robust growth.
- Regularly monitor and remove any weeds that may compete with the seedlings for nutrients and resources.
- Keep an eye out for common pests such as aphids or slugs and take appropriate measures to control them.
- Maintain good air circulation by thinning out overcrowded seedlings.
- Continuously monitor the soil moisture and adjust watering accordingly to prevent over or under watering.
Monitoring Growth And Development
Keep track of the growth and development of your lettuce seedlings to ensure optimal conditions. Here’s what you need to keep an eye on:
- Monitor the height and width of the seedlings as they should gradually increase over time.
- Observe leaf color, which should be vibrant green and healthy-looking.
- Watch for any signs of discoloration, wilting, or spotting, as these may indicate nutrient deficiencies or pest issues.
- Measure the spacing between the seedlings to ensure they have enough room to grow without overcrowding each other.
- Regularly check the moisture level of the soil to prevent both overwatering and underwatering.
- Assess the overall health of the seedlings by looking for signs of stunted growth or yellowing leaves.
Remember, providing proper care, diligent monitoring, and timely actions will contribute to healthy lettuce seedling growth.
Vegetative Stage
Leaf Expansion And Growth:
During the vegetative stage of lettuce growth, the focus is on the expansion and growth of leaves. This stage is crucial in establishing a strong foundation for the plant. Here are some key points to understand about the leaf expansion and growth phase:
- Leaf initiation: The vegetative stage starts with the emergence of the first true leaves after the cotyledons. These leaves have a distinct shape and are responsible for capturing sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Leaf size: As the plant continues to grow, the size of the leaves also increases. Leaf expansion occurs as the cells within the leaves expand and replicate. This process is essential for maximizing the plant’s ability to absorb light energy.
- Leaf arrangement: Lettuce leaves are typically arranged in a rosette pattern, with the younger leaves situated in the center and the older leaves surrounding them. This arrangement allows for optimal light exposure and efficient use of space.
- Leaf color: The color of lettuce leaves can vary depending on the variety. Generally, healthy lettuce leaves exhibit a vibrant green color, indicating an active process of photosynthesis.
Nutrient Requirements:
To support healthy growth during the vegetative stage, lettuce plants have specific nutrient requirements. Providing the necessary nutrients is essential for optimal leaf expansion and overall plant development. Here are the key nutrient requirements for lettuce during the vegetative stage:
- Nitrogen (n): Lettuce plants require a sufficient supply of nitrogen as it plays a vital role in promoting leaf growth. Nitrogen supports chlorophyll production and enhances the plant’s ability to convert sunlight into energy.
- Phosphorus (p): Adequate phosphorus levels are essential for root development during the vegetative stage. Phosphorus also aids in energy transfer and the formation of essential compounds within the plant.
- Potassium (k): Potassium is crucial for overall plant health and plays a role in cell growth and photosynthesis. It helps increases disease resistance and enhances the plant’s ability to withstand environmental stressors.
- Micronutrients: In addition to the macronutrients mentioned above, lettuce plants also require various micronutrients such as iron, zinc, manganese, and others for healthy leaf expansion. These micronutrients are involved in different physiological processes and are vital for optimal growth.
Watering And Irrigation:
Proper watering and irrigation are essential in the vegetative stage to ensure that lettuce plants receive enough moisture for optimal leaf expansion and growth. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to watering and irrigation:
- Moisture consistency: Lettuce plants thrive in consistently moist soil. It is important to avoid both overwatering and underwatering. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can stunt growth and affect leaf development.
- Frequency of watering: Lettuce plants typically require frequent watering, especially during hot weather conditions. As a general guideline, aim to keep the soil evenly moist but not overly saturated.
- Irrigation methods: There are various irrigation methods that can be used for lettuce, including drip irrigation, sprinkler systems, or hand-watering. The chosen method should ensure that water is delivered directly to the root zone and not sprayed onto the leaves.
- Water quality: Lettuce plants are sensitive to water quality. It is advisable to use clean, preferably filtered, water to avoid exposing the plants to any harmful substances that might be present in tap water.
By understanding the leaf expansion and growth, nutrient requirements, and proper watering practices during the vegetative stage, you can provide optimal conditions for lettuce plants to thrive and develop into healthy, productive crops.
Harvesting And Beyond
Lettuce Growth Stages – Harvesting And Beyond
After weeks of nurturing your lettuce plants, it’s finally time to reap the rewards of your efforts. Harvesting lettuce at the right stage is crucial for getting the tastiest leaves while ensuring a continuous supply throughout the growing season. In this section, we’ll explore the determining factors for lettuce readiness, proper harvesting techniques, and post-harvest care and storage to help you make the most of your lettuce crop.
Determining Readiness For Harvest
Determining when your lettuce is ready to be harvested requires a keen eye and a gentle touch. Here are some indicators to look out for:
- Size: Lettuce leaves should have reached a size suitable for consumption. Different lettuce varieties have varying sizes at maturity, so refer to the seed packet or plant label for specific guidelines.
- Color and texture: The color of lettuce leaves can vary depending on the variety. Look for vibrant, healthy-looking leaves without any signs of wilting or browning. The texture should be crisp and tender.
- Leaf appearance: Lettuce leaves should have their characteristic shape and structure. Avoid harvesting if the leaves have become elongated, tough, or bitter, as this indicates that the lettuce has bolted and reached the end of its prime stage.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
Now that you’ve determined that your lettuce is ready for harvest, it’s time to pick those fresh and delicious leaves. Here are some proper techniques to ensure a successful harvest:
- Use clean, sharp tools: Always use clean and sharp scissors or garden shears to minimize damage to the plant. This helps maintain the overall health of the lettuce and allows for regrowth.
- Harvesting individual leaves: For a continuous supply of lettuce, you can start by harvesting the outer leaves one by one. This allows the inner leaves to continue growing for future harvests.
- Harvesting the whole head: If you prefer harvesting the entire lettuce head, cut it off at the soil level, just above the base of the plant. Remove any soil or debris before storing.
Post-Harvest Care And Storage
To prolong the freshness and quality of your harvested lettuce, it’s essential to provide proper post-harvest care and storage. Follow these tips for optimal results:
- Cleaning: Gently rinse the lettuce leaves with cold water to remove any dirt or insects. Avoid soaking them, as excessive moisture can lead to spoilage.
- Drying: After rinsing, pat the leaves dry with a clean kitchen towel or use a salad spinner. Excess moisture can promote wilting and encourage the growth of bacteria.
- Storage containers: Place the lettuce leaves in a breathable storage container, such as a plastic bag with small holes or a perforated vegetable bag. This helps maintain the right moisture balance and prevents excess moisture buildup, which can lead to rotting.
- Refrigeration: Store the lettuce in the refrigerator’s crisper drawer, where the temperature is slightly cooler and the humidity is higher. It’s best to consume the lettuce within a week to ensure optimal freshness and flavor.
By following these tips for determining readiness, using proper harvesting techniques, and providing appropriate post-harvest care and storage, you can enjoy fresh and delicious lettuce from your garden for weeks to come. Remember, the key is to maintain the lettuce’s quality by harvesting at the right stage and storing it properly.
Now, it’s time to savor the fruits (or leaves) of your labor!
Common Pests And Diseases
Lettuce plants can sometimes face challenges in the form of pests and diseases. It is important for gardeners to be aware of common issues that can arise so that they can take proactive measures to prevent and control them. In this section, we will discuss the identification and prevention of common pests and diseases and provide treatment options if they occur.
Identification And Prevention:
- Aphids: These small insects can be found on the undersides of lettuce leaves and can cause damage by feeding on the sap. To prevent aphid infestations:
- Inspect plants regularly and remove any affected leaves.
- Introduce natural predators like ladybugs or lacewings to control aphid populations.
- Use insecticidal soaps or neem oil if necessary.
- Slugs and snails: These slimy creatures can cause significant damage to lettuce plants by feeding on the leaves. To prevent slug and snail damage:
- Remove any debris or hiding places around the garden.
- Set up traps using beer or copper barriers to deter them.
- Handpick slugs and snails and dispose of them.
- Powdery mildew: This fungal disease appears as a white powdery coating on the leaves, inhibiting photosynthesis and weakening the plant. To prevent powdery mildew:
- Ensure good air circulation by spacing plants appropriately.
- Avoid overhead watering to prevent water accumulation on foliage.
- Apply fungicides if necessary, following the instructions carefully.
- Downy mildew: Unlike powdery mildew, downy mildew appears as yellow or pale green spots on the leaves, which can eventually turn brown. To prevent downy mildew:
- Avoid overcrowding by providing adequate spacing between plants.
- Water the plants at the base rather than overhead.
- Apply a copper-based fungicide to control the spread.
Treatment Options:
- Whitefly: These tiny white insects can be found on the undersides of leaves, sucking sap and excreting honeydew, leading to sooty mold development. To treat whitefly infestations:
- Use yellow sticky traps to monitor and capture adult whiteflies.
- Introduce natural enemies, such as encarsia formosa, to control populations.
- Apply insecticidal soaps or neem oil if necessary.
- Fusarium wilt: This soil-borne fungal disease causes yellowing, wilting, and stunted growth of lettuce plants. To address fusarium wilt:
- Use disease-resistant varieties of lettuce if available.
- Rotate crops to prevent the buildup of the pathogen in the soil.
- Dispose of infected plants properly to prevent further spread.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to managing pests and diseases in lettuce. Regular monitoring, maintaining good garden practices, and taking swift action when necessary can help ensure healthy lettuce plants and a bountiful harvest.
Tips For Successful Lettuce Growth
Choosing Suitable Lettuce Varieties:
- There are various lettuce varieties to choose from, each with its own growth habits, flavors, and textures.
- Consider factors such as the climate, growing season, and available space when selecting lettuce varieties.
- Popular lettuce varieties include butterhead, romaine, loose-leaf, and crisphead lettuce.
- Butterhead lettuce is known for its soft and tender leaves, while romaine lettuce has a crunchy texture. Loose-leaf lettuce offers a variety of colors and flavors, and crisphead lettuce forms tight heads.
- Choose lettuce varieties that are well-suited for your desired growth conditions, such as heat-tolerant varieties for summer planting or cold-hardy varieties for winter planting.
Utilizing Succession Planting:
- Succession planting involves sowing lettuce seeds in batches at regular intervals to ensure a continuous supply of fresh lettuce throughout the growing season.
- Start by planting the first batch of lettuce seeds, and then plant subsequent batches every two to three weeks.
- Succession planting allows for a staggered harvest, reducing the risk of a surplus of lettuce that may go to waste.
- It also helps manage pest and disease problems, as you can quickly remove any infected plants and replant new ones.
- Make sure to plan your succession planting schedule based on the maturity date of the lettuce variety you choose.
Implementing Mulching And Companion Planting Strategies:
- Mulching around lettuce plants helps conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
- Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as straw or shredded leaves, around the base of lettuce plants while avoiding direct contact with the stems.
- Mulching also helps prevent soil splashback onto leaves, reducing the risk of soil-borne diseases.
- Companion planting involves growing compatible plants alongside lettuce to enhance growth and deter pests.
- Some suitable companion plants for lettuce include herbs like basil and dill, which can repel pests like aphids and attract beneficial insects.
- Avoid planting lettuce near crops that are susceptible to the same pests or diseases to minimize risk.
Remember, choosing suitable lettuce varieties, utilizing succession planting, and implementing mulching and companion planting strategies are key to successful lettuce growth. Applying these tips can help you grow healthy, flavorful lettuce throughout the year. So go ahead and cultivate your own lettuce patch with confidence!
Frequently Asked Questions For Lettuce Growth Stages
How Long Does It Take For Lettuce To Grow?
On average, lettuce takes about 50 to 70 days to reach maturity, depending on the variety. However, some lettuce varieties can be harvested as early as 30 days if you prefer baby greens.
Conclusion
To summarize, understanding the growth stages of lettuce is crucial for successful cultivation. From the germination stage, where the seeds sprout, to the seedling stage, where the young plants develop leaves, and finally to the maturity stage, where the lettuce is fully grown and ready to harvest, each phase requires specific care and attention.
Providing adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients at the right time is crucial for optimal growth. Adjusting the temperature and humidity levels in controlled environments like greenhouses can also promote healthy growth. Additionally, pests and diseases should be closely monitored and promptly addressed to ensure the overall health of the lettuce plants.
By following these guidelines, growers can expect a bountiful harvest of fresh, crisp lettuce. So whether you are a novice gardener or an experienced grower, mastering the lettuce growth stages is essential to bring the best out of your greens and enjoy the taste of success.
© 2024 Lotusmagus.com. All rights reserved. This content is protected by copyright. Visit Lotusmagus.com for more information.

