The disadvantages of plant growth regulators include potential toxicity to the environment and unintended effects on non-target organisms. Plant growth regulators can have negative impacts on biodiversity and may disrupt ecosystems.

Credit: griffinfertilizer.com
Negative Effects On Environment
Impact On Ecosystem
Plant growth regulators can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting various species.
- Loss of biodiversity due to altered plant growth patterns.
- Disruption in food chains and ecosystem stability.
- Negative impact on natural habitats and wildlife populations.
Residual Effects On Soil
The use of plant growth regulators can leave long-lasting effects on soil quality.
- Decreased soil fertility leading to poor crop yields.
- Soil contamination with chemical residues affecting future plant growth.
- Disruption of soil microorganisms, crucial for nutrient cycling.
Agricultural Concerns
Plant growth regulators in agriculture can have certain drawbacks. Excessive use may result in stunted growth, poor fruit quality, and increased susceptibility to diseases. Additionally, it can impact the environment and human health. Careful monitoring and judicious application of these regulators are crucial to minimize the potential disadvantages.
Pesticide Resistance
A major concern associated with the use of plant growth regulators (PGRs) in agriculture is the development of pesticide resistance. PGRs are chemicals that manipulate plant growth and development, and they are often used in combination with pesticides to enhance their effectiveness. However, over time, repeated exposure to PGRs can lead to the development of resistance in target plant species. This means that the same PGRs that were once effective in controlling plant growth may no longer be effective, requiring the use of higher doses or alternative PGRs.
Pesticide resistance can have significant consequences for crop production. It can limit the effectiveness of pest management strategies, making it more difficult for farmers to control weeds, insects, and diseases. This can result in reduced crop yields and increased economic losses for farmers. Furthermore, the development of resistance can also lead to the proliferation of more aggressive and hard-to-control weed species, causing long-term ecological disruptions in agricultural ecosystems.
Effect On Non-target Species
Another agricultural concern associated with the use of PGRs is their potential impact on non-target species. PGRs are designed to specifically target certain aspects of plant growth and development, but there is always the risk of unintended effects on other organisms in the environment. These non-target species can include beneficial insects, pollinators, and even neighboring crops or plants.
The use of PGRs can inadvertently harm beneficial insects such as bees, which play a crucial role in pollination and maintaining healthy ecosystems. If PGRs are not carefully targeted and applied, they may also drift onto neighboring crops or plants, causing unintended damage. This can lead to crop losses and economic setbacks for farmers, as well as potential ecological imbalances in the surrounding environment.
Human Health Risks
Plant growth regulators in agriculture pose potential human health risks due to chemical exposure. Overuse can lead to respiratory issues, skin irritations, and long-term health consequences. Monitoring and proper handling are crucial to mitigate these disadvantages.
Toxicity Concerns
Exposure to Poisonous Chemicals
One of the main disadvantages of plant growth regulators is the potential toxicity concerns they pose to human health. These regulators contain chemicals that are designed to manipulate plant growth and development, but they can also be harmful to humans.
When these regulators are applied to crops, there is a risk of direct exposure to the chemicals for farmers and agricultural workers who handle and apply the products. These chemicals can be absorbed through the skin or inhaled, potentially leading to adverse health effects.
Short-term exposure to high levels of plant growth regulators can cause symptoms such as skin irritation, eye irritation, respiratory distress, and even systemic toxicity.
Long-Term Health Effects
Additionally, long-term exposure to plant growth regulators may have serious health implications. Studies have suggested potential links between prolonged exposure to certain regulators and increased risk of conditions such as cancer, reproductive problems, and developmental disorders.
Research on the effects of plant growth regulators on human health is still ongoing, and more data is needed to fully understand their long-term impact. However, the existing evidence raises valid concerns about the potential risks they may pose.
Residue In Food
Traceability Challenges
Another human health risk associated with plant growth regulators is the potential residue they leave behind on crops. Even if the regulators are applied according to recommended guidelines and in compliance with safety regulations, residue may still be present.
This can pose challenges in terms of traceability, as the presence of residue can be difficult to detect and quantify. This raises concerns about the inadvertent consumption of these chemicals by the general population through food and beverages.
Unknown Effects on Human Health
Since plant growth regulators are relatively new, there is limited research regarding their overall safety for human consumption. The long-term effects of ingesting residual regulators are not yet fully understood.
While regulatory bodies set limits for pesticide residues, the impact of plant growth regulators on human health is still a subject of ongoing study and scientific inquiry. The potential risks and consequences of regular exposure to these residues remain uncertain.
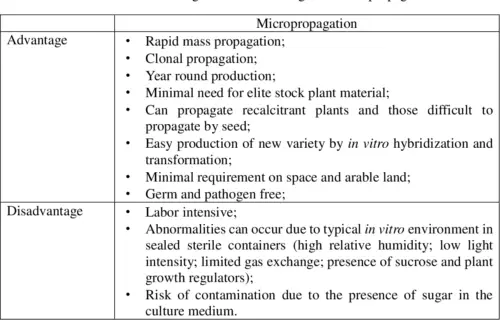
Credit: www.semanticscholar.org
Regulatory Challenges
Ethical Considerations
Plant growth regulators have been widely used in agriculture to enhance yields and improve crop quality. However, their usage raises ethical concerns related to the manipulation of growth and its impact on natural processes.
Manipulation Of Growth
The use of plant growth regulators to control plant growth and development may be perceived as human interference with the natural order of biological processes. This manipulation raises questions about the genetic integrity of plant species and the potential for creating unnatural or unstable genetic variations. Such actions can be considered as disrupting the balance of nature.
Impact On Natural Processes
Plant growth regulators can alter the natural growth patterns and responses of plants, potentially causing ecological disturbances. These substances may also have unintended effects on non-target organisms, disrupting ecosystem balance and biodiversity.
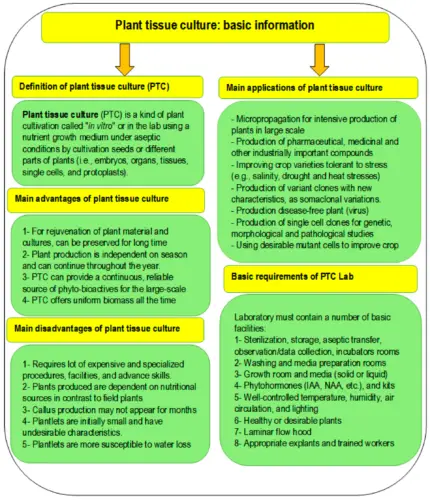
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Frequently Asked Questions For What Are The Disadvantages Of Plant Growth Regulators?
What Are The Disadvantages Of Pgr?
The drawbacks of PGR include potential harm to the environment, increased health risks, reduced biodiversity, and potential harm to beneficial insects. PGRs may also result in the development of resistance in pests and disease-causing organisms, leading to the need for higher doses or alternative treatments.
What Are The Problems With Pgr?
PGR can have several problems, which include potential health and environmental risks, excessive plant growth leading to weak stems, reduced fruit quality and taste, and the possibility of residue on produce.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Artificial Plant Growth Regulators?
Artificial plant growth regulators can harm the environment, disrupt natural processes, impact biodiversity, and may lead to chemical residue in crops.
What Are The Risks Of Pgr?
PGRs can pose risks such as overgrowth, reduced fruit quality, and environmental impact. It’s crucial to follow proper guidelines and dosage to minimize adverse effects. Regular monitoring and expert guidance can help mitigate potential risks associated with PGR use.
Conclusion
Despite their benefits, plant growth regulators have drawbacks to consider. These include environmental risks, potential harm to non-target organisms, and regulatory restrictions. Being aware of these disadvantages is crucial for sustainable agriculture practices and balanced plant growth management. Make informed decisions to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
