Plant hormones are naturally occurring chemical messengers that regulate plant growth and development, while plant growth regulators are synthetic substances that mimic the action of natural hormones to manipulate plant growth. Plant hormones are endogenous compounds produced by plants to coordinate various physiological processes, whereas plant growth regulators are exogenous substances applied to control growth patterns, flowering, or fruit development.
Both plant hormones and growth regulators play critical roles in the regulation of plant growth, development, and response to environmental stimuli. Understanding the differences between these substances is essential for effective horticultural practices and agricultural management. We will explore the distinct characteristics of plant hormones and plant growth regulators, their functions, and their applications in agriculture and horticulture.
Credit: in.pinterest.com
Plant Hormones And Plant Growth Regulators
Plant hormones and plant growth regulators are often used interchangeably, but there is a slight difference between the two. Plant hormones are naturally occurring substances produced by plants, while plant growth regulators are synthetic substances that mimic the effects of plant hormones.
Both play a crucial role in regulating plant growth and development.
Plant Hormones
Plant hormones are signaling molecules that regulate various processes within plants.
They control growth, development, and response to environmental factors in plants.
Plant Growth Regulators
Plant growth regulators are chemicals that can alter the growth and development of plants.
They are synthetic substances that mimic the action of natural plant hormones.
Functions Of Plant Hormones
Plant hormones and plant growth regulators play significant roles in regulating various physiological processes in plants. Understanding the functions of plant hormones is essential for effective plant growth management and crop production. Let’s explore the specific functions of each plant hormone:
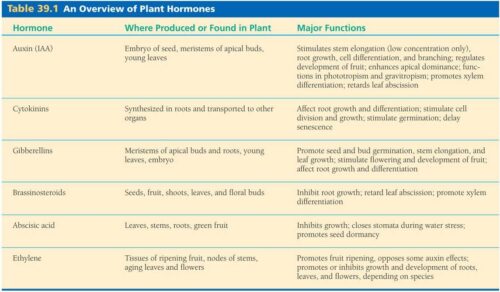
Auxins
Auxins are responsible for controlling plant growth, particularly in the elongation of cells and the development of new leaves and roots. They also play a crucial role in phototropism and gravitropism.
Gibberellins
Gibberellins are involved in promoting stem and leaf elongation, seed germination, and flowering. They also regulate the development of fruits and help in breaking seed dormancy.
Cytokinins
Cytokinins promote cell division and are essential for overall plant growth and development. They also delay the aging of plant tissues and help in the formation of chloroplasts.
Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid functions in stress responses, particularly in processes such as seed dormancy, stomatal closure to prevent water loss, and regulation of plant responses to environmental stresses such as drought and salinity.
Ethylene
Ethylene is involved in the regulation of fruit ripening, flower senescence, and abscission (the shedding of leaves, flowers, and fruits). It also has roles in responses to biotic and abiotic stress.
Effects Of Plant Growth Regulators
Plant hormones are naturally occurring substances in plants that regulate growth and development, while plant growth regulators are man-made chemicals that mimic these hormonal effects. The main difference lies in their origin, with hormones being natural and regulators being synthetic.
Effects of Plant Growth Regulators —————————- Plant growth regulators (PGRs) are essential for the development and growth of plants. They play a crucial role in controlling various aspects of plant growth, including cell division, elongation, differentiation, and flowering. Understanding the effects of plant growth regulators helps us recognize their significance in agriculture and horticulture. Let’s delve into the specific effects of plant growth regulators, including their ability to inhibit growth, promote growth, and modify plant responses. Inhibiting Growth —————————-
Inhibiting Growth
Plant growth regulators, such as abscisic acid, can inhibit plant growth under unfavorable conditions, such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. This hormone helps conserve water by closing stomata, reducing transpiration and photosynthesis, thereby slowing down plant growth. Promoting Growth —————————-
Promoting Growth
Gibberellins are plant growth regulators that promote growth by stimulating cell elongation, seed germination, and flowering. They are particularly crucial for promoting stem elongation, which is essential for plant height and internode length. Modifying Plant Responses —————————-
Modifying Plant Responses
Auxins are plant growth regulators that modify plant responses by influencing cell elongation, apical dominance, and root initiation. They are also involved in phototropism and gravitropism, directing plant growth in response to light and gravity stimuli, respectively. Understanding the effects of plant growth regulators helps us harness their potential for improving crop yield, managing plant growth, and enhancing overall plant health. This in-depth understanding of plant hormones and growth regulators can significantly influence agricultural practices, ultimately leading to more efficient and sustainable plant production.

Credit: slideplayer.com
Sources Of Plant Hormones And Growth Regulators
Plant hormones and growth regulators play vital roles in the growth and development of plants. They can be sourced from different origins, including naturally occurring sources and synthetic sources.
Naturally Occurring Sources
- Plant tissues: Cells and tissues within the plant itself produce hormones.
- Soil: Microorganisms in the soil can also contribute to the production of plant hormones.
- Plant extracts: Substances extracted from plants can contain natural growth regulators.
Synthetic Sources
- Laboratories: Scientists can synthesize plant hormones and growth regulators in controlled environments.
- Chemicals: Some growth regulators are chemically formulated for specific purposes.
- Biotechnological processes: Advances in biotechnology enable the production of synthetic growth regulators.
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Naturally Occurring Sources | – Plant tissues |
| – Soil microorganisms | |
| – Plant extracts | |
| Synthetic Sources | – Laboratories |
| – Chemicals | |
| – Biotechnological processes |
Applications Of Plant Hormones And Growth Regulators
Plant hormones and growth regulators play vital roles in various fields, including agriculture, gardening, plant propagation, tissue culture, and crop yield enhancement. Understanding their applications is essential for harnessing their potential to benefit plants and crops. Let’s explore how these plant hormones and growth regulators are utilized in different areas:
Agriculture And Gardening
In agriculture and gardening, plant hormones and growth regulators are utilized to regulate plant growth and development, improve crop yield, and manage pest control.
- Promoting plant growth: Plant hormones like auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins are commonly used to stimulate root development, enhance shoot growth, and increase plant vigor.
- Controlling flowering and fruit ripening: Plant growth regulators such as ethylene are applied to manipulate flowering time and encourage fruit ripening.
- Managing pests and diseases: Some plant hormones can be used to induce systemic resistance in plants, making them more resistant to pests and diseases.
Plant Propagation And Tissue Culture
Plant hormones and growth regulators also play a significant role in plant propagation and tissue culture techniques.
- Promoting root formation: Auxins are commonly used for root initiation during the cutting propagation of plants.
- Inducing callus formation: Plant growth regulators like auxins and cytokinins are used to induce callus formation, a crucial step in tissue culture.
- Regulating somatic embryogenesis: Plant hormones are carefully manipulated to induce somatic embryo formation, which is essential for micropropagation and plant tissue engineering.
Crop Yield Enhancement
Plant hormones and growth regulators also find application in enhancing crop yield through various methods.
- Improving fruit setting and development: Plant growth regulators like gibberellins and auxins can be used to enhance fruit setting, size, and quality, leading to increased crop yield.
- Managing plant stress: Plant hormones help in managing stress caused by environmental factors such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures, thus improving crop productivity.
- Increasing nutrient uptake: Plant hormones are utilized to enhance nutrient uptake efficiency, leading to better nutrient utilization and increased crop yield.
Understanding the applications of plant hormones and growth regulators in agriculture, gardening, plant propagation, tissue culture, and crop yield enhancement is crucial for maximizing plant productivity, improving crop quality, and ensuring sustainable agriculture practices.

Credit: www.slideserve.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Difference Between Plant Hormones And Plant Growth Regulators?
What Is The Difference Between Plant Hormones And Plant Growth Regulators Brainly?
Plant hormones are naturally occurring substances produced by plants to control growth and development. Plant growth regulators, on the other hand, are synthetic compounds that mimic the actions of plant hormones.
Why Plant Hormones Are Called Growth Regulators?
Plant hormones are called growth regulators because they control plant growth and development. They regulate various processes such as cell division, elongation, and differentiation. These hormones play a crucial role in shaping the overall growth and response of plants to environmental stimuli.
What Is A Plant Growth Regulator?
A plant growth regulator is a substance that controls plant processes, like growth and development, to enhance desired traits.
What Is The Difference Between Plant Growth Regulators And Fertilizers?
Plant growth regulators and fertilizers serve different purposes. Plant growth regulators control plant growth and development, while fertilizers provide essential nutrients for plant growth. Plant growth regulators influence processes like root growth, flowering, and fruiting, while fertilizers supply nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for healthy plant growth.
Conclusion
In essence, plant hormones naturally occur, while plant growth regulators are synthetically made. Understanding their distinctions helps in regulating plant growth effectively. By comprehending these differences, gardeners and farmers can make informed decisions to optimize plant health and development for better yields.
