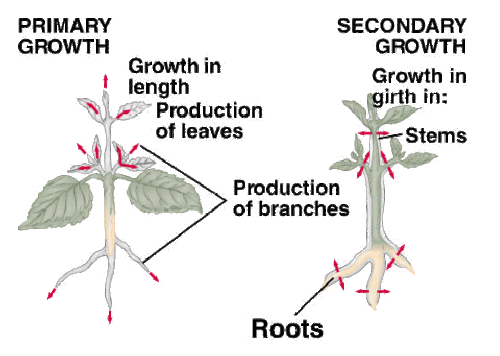
Primary plant increase refers back to the lengthening of roots and shoots, while secondary growth ends in the thickening of stems and roots. Primary increase happens on the apical meristems, answerable for growing plant duration, while secondary growth takes area at the lateral meristems, main to plant girth.
Understanding the difference among those two varieties of boom is essential for comprehending the general development and shape of flora. It allows for effective cultivation practices and aids within the development of stepped forward plant types. We will delve deeper into the differences between primary and secondary plant increase, dropping light on their distinct techniques and importance within the boom and improvement of vegetation.
Understanding these techniques can provide treasured insights into plant biology and make contributions to advancements in agricultural strategies and plant breeding.
Primary Plant Growth
Primary plant increase refers to the preliminary growth phase of a plant, that specialize in growing the duration of stems and roots.
Cell Division In Primary Growth
Cell division in number one increase involves the rapid multiplication of plant cells to facilitate increase.
Cell Elongation In Primary Growth
During primary growth, cellular elongation takes place, main to the lengthening of roots and stems.
Cell Differentiation In Primary Growth
Cell differentiation in number one increase is the method where cells end up specialized for unique capabilities within the plant.
Credit: cas.Miamioh.Edu
Secondary Plant Growth
Secondary plant growth, additionally referred to as lateral growth, is the system by using which flora growth their girth and thickness after accomplishing a positive level of number one increase. This type of boom is fundamental for the improvement and structural guide of the plant, and it occurs in unique areas of the plant’s frame, often in the stems and roots.
Formation Of Lateral Meristems
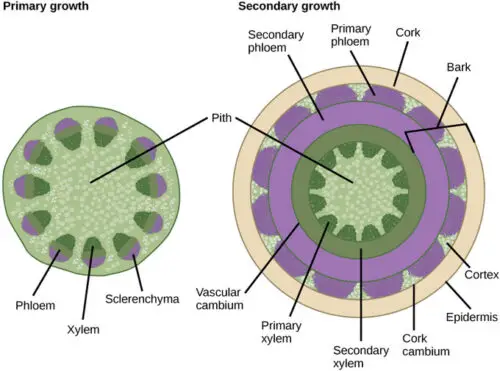
Lateral meristems are the important thing gamers in secondary growth. They are liable for the manufacturing of recent cells that contribute to the enlargement of the plant’s width. There are principal types of lateral meristems: the vascular cambium, which generates secondary vascular tissues, and the cork cambium, which offers upward push to the outer protecting layers of the plant.
Cambial Activity In Secondary Growth
The cambium is a layer of undifferentiated cells discovered in the stems and roots of vascular plants. During secondary growth, the cambium turns into active, dividing and producing new cells that differentiate into secondary xylem and phloem tissues, contributing to the plant’s multiplied diameter and potential for nutrient transport.
Secondary Growth In Stem And Root
In stems, secondary increase outcomes inside the thickening of the stem, permitting it to assist the burden of the plant and store reserve substances. This growth is crucial for the durability and stability of woody flora. In roots, secondary growth complements the uptake of water and vitamins from the soil and offers anchorage for the plant.
Differences Between Primary And Secondary Growth
The variations between number one and secondary growth in plant life play a essential role in knowledge their improvement and physiology. Let’s delve into the awesome traits that set those two kinds of boom aside.
Origin Of Growth
Primary growth originates from the apical meristems positioned at the tips of the plant shoots and roots. In contrast, secondary boom arises from the lateral meristems inclusive of the vascular cambium and cork cambium, which are chargeable for the thickening of stems and roots.
Location Of Growth
Primary boom happens at the apical and root meristems, contributing to the plant’s top and root length. On the alternative hand, secondary boom specially takes place in the vascular tissues, main to an increase within the girth or diameter of stems and roots.
Types Of Tissues Involved
Primary growth involves the protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium, leading to the formation of dermal, ground, and vascular tissues. In assessment, secondary boom generally impacts the vascular cambium, cork cambium, and secondary meristematic tissues, fostering the development of secondary xylem and phloem in addition to cork cells.
Growth Patterns
Primary increase reveals an acropetal increase sample, in which the youngest cells are at the pinnacle, and the oldest are at the lowest. Meanwhile, secondary boom showcases a simultaneous radial growth pattern, resulting inside the formation of annual jewelry in woody plants.

Credit: pediaa.Com
Importance Of Primary And Secondary Growth
Primary and secondary growth are crucial techniques in a plant’s lifecycle. Each plays a important position in ensuring the plant’s general shape and feature.
Primary Growth: Development Of Plant
Primary growth focuses on the plant’s vertical increase and improvement. This process facilitates in establishing the plant’s fundamental shape, from roots to shoots.
Secondary Growth: Increase In Girth And Strength
Secondary growth entails the increase in girth and strength of the plant. It contributes to the plant’s capacity to assist itself and face up to outside forces.
Examples Of Primary And Secondary Growth
Primary and secondary growth are two types of plant increase. Primary growth is liable for the elongation of stems and roots, even as secondary growth is responsible for the boom in thickness of stems and roots. The important distinction among the two is that primary increase happens within the apical meristem, positioned on the tip of the stem or root, while secondary boom occurs inside the lateral meristem, placed inside the cambium layer of the stem or root.
Primary and secondary boom are critical procedures that contribute to the boom and development of vegetation. While primary boom permits plants to boom their duration, secondary increase aids in enlarging their girth. Let’s explore a few examples of number one and secondary boom in vegetation.
Example Of Primary Growth: Shoot Elongation
One example of number one growth in plant life is shoot elongation. During this method, the shoot of a plant grows longer, allowing it to attain new heights. The increase happens on the apical meristems, which can be observed on the recommendations of the shoots. These meristems incorporate undifferentiated cells that actively divide, main to the elongation of the shoot.
In shoot elongation, the cells near the apical meristem go through fast mobile division and elongation. As a result, the plant’s shoot will become longer, allowing it to get entry to greater sunlight, vitamins, and water. Shoot elongation is specially important for plants that depend upon photosynthesis as their foremost source of power.
Key Points:
- Primary boom is accountable for shoot elongation in plant life.
- Apical meristems incorporate undifferentiated cells that actively divide.
- Shoot elongation lets in plants to get entry to greater sunlight, vitamins, and water.
- Secondary boom is chargeable for tree trunk enlargement in plant life.
- Lateral meristems, along with vascular cambium and cork cambium, play critical roles.
- Growth jewelry in tree trunks serve as statistics of plant increase.
Example Of Secondary Growth: Tree Trunk Enlargement
Tree trunk growth is an example of secondary growth. Unlike primary growth, which mostly focuses on elongating shoots, secondary growth aids within the thickening of plant structures, which includes the tree trunk. This type of growth occurs in the lateral meristems, which might be responsible for growing the girth of the plant.
The lateral meristems, consisting of the vascular cambium and cork cambium, play vital roles in secondary growth. The vascular cambium allows generate new layers of xylem and phloem, contributing to the increase rings visible in tree trunks. On the alternative hand, the cork cambium generates cork cells, which function a defensive outer layer.
Through secondary increase, the tree trunk progressively enlarges, imparting structural help to the developing plant. It also enables the transport of water and nutrients all through the plant body. The boom rings seen within the move-phase of a tree trunk serve as a record of the plant’s increase over the years.
Key Points:
Credit: bio.Libretexts.Org
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is The Difference Between Primary And Secondary Plant Growth?
What Is The Primary Growth Of A Plant?
The primary growth of a plant takes place on the recommendations of stems and roots. This growth is liable for growing plant height and root period.
What Is The Difference Between Primary And Secondary Roots?
Primary roots expand at once from the seed, helping plant boom. Secondary roots stand up from primary roots, imparting additional help.
What Is The Difference Between Primary And Secondary Growth Quizlet?
Primary boom refers to the vertical increase of a plant, even as secondary increase entails the growth in girth or width. The number one growth happens inside the apical meristems, even as the secondary increase happens in the lateral meristems. Both tactics contribute to the overall boom and improvement of the plant.
What Is The Secondary Growth Of A Plant?
Secondary increase of a plant is the increase in width, resulting in thicker stems and roots. It happens in woody flowers through lateral meristems.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference among primary and secondary plant increase is important for botany enthusiasts. Observing the differences in tissue formation and traits affords treasured insights into plant improvement. By recognizing those boom procedures, we benefit a deeper appreciation of the complexity of plant biology.
Explore similarly into this captivating situation to enhance your botanical information.
