Wheat growth stages can be categorized into different phases such as germination, vegetative, reproductive, and ripening. The growth stages of wheat are crucial for understanding the plant’s development and managing its cultivation effectively.
Wheat is a cereal grain widely grown across the world and is a staple food for many. Its growth stages comprise distinct periods that contribute to its overall development and yield. Understanding these stages is essential for farmers and agronomists to monitor and manage their crops properly.
Wheat growth stages can be divided into four main phases: germination, vegetative, reproductive, and ripening. Each phase has unique characteristics and requirements, and proper care and attention during each stage are crucial for achieving optimal yield. This article will explore the different growth stages of wheat and their significance in crop management.
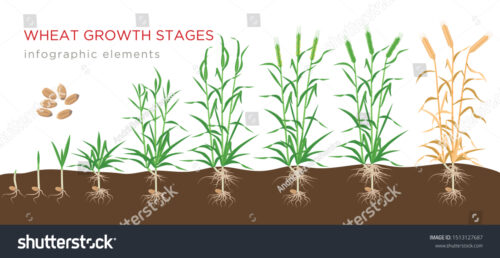
Understanding The Different Growth Phases Of Wheat
Wheat growth stages play a crucial role in ensuring a successful harvest for farmers. Monitoring and understanding these growth stages can provide valuable insights into the crop’s health, allowing farmers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
In this section, we will explore the significance of monitoring wheat growth stages and why they matter for farmers.
Significance Of Monitoring Wheat Growth Stages
Monitoring wheat growth stages is essential for farmers to optimize crop management strategies and maximize their yields. By closely observing the growth stages, farmers can:
- Identify the optimal time for irrigation: Different growth stages require varying levels of moisture. Monitoring the growth stages helps farmers determine when to provide the necessary irrigation, preventing both over and under watering.
- Determine the appropriate fertilizer application: Each growth stage requires specific nutrients for optimal growth. By monitoring these stages, farmers can apply the right type and amount of fertilizer at the right time, ensuring healthy plant development.
- Assess pest and disease risks: Certain pests and diseases are more prevalent during specific growth stages. By monitoring the growth stages, farmers can be proactive in implementing preventive measures, such as employing appropriate pest control strategies or disease-resistant crop varieties.
- Plan harvesting activities: The growth stages provide insight into the maturation of the wheat crop. This information helps farmers plan harvesting activities and estimate the optimal time for maximum yield and nutritional value.
Understanding the significance of monitoring wheat growth stages empowers farmers to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions at each stage, optimizing crop health and productivity.
Why Wheat Growth Stages Matter For Farmers
Wheat growth stages matter for farmers due to the following reasons:
- Yield optimization: Monitoring and managing growth stages contribute to maximizing wheat yields. Farmers can apply timely interventions, such as adjusting irrigation or applying necessary treatments, to promote strong and healthy growth, ultimately leading to higher yields.
- Resource efficiency: By understanding the growth stages, farmers can allocate resources more efficiently. They can minimize water usage, reduce fertilizer waste, and optimize pesticide applications by tailoring them to the specific growth stages that require intervention.
- Risk mitigation: Early detection and management of potential issues, such as pests or diseases, are critical to prevent significant crop damage. By monitoring wheat growth stages, farmers can identify any deviations from normal development and implement suitable preventive or corrective measures promptly.
- Quality control: Different growth stages impact the quality characteristics of wheat, including kernel size, protein content, and gluten development. By closely monitoring the growth stages, farmers can ensure that the wheat meets the desired specifications for specific end-uses, such as baking or milling.
Understanding the different growth stages of wheat is essential for farmers to optimize their crop management practices, improve resource efficiency, mitigate risks, and maximize the quality and quantity of their yields. By monitoring and responding to the specific needs of each growth stage, farmers can cultivate healthy and productive wheat crops.
Germination Stage: From Seed To Seedling
Overview Of Germination In Wheat Seeds
Germination is an essential stage in the life cycle of wheat seeds, marking the transition from a dormant state to an active growth phase. During germination, the seed absorbs water and swells, allowing the embryo within to develop into a seedling.
Factors Influencing Germination Process
The germination process in wheat seeds can be influenced by various factors. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Seed quality: The quality of the seed plays a significant role in germination. Seeds that are damaged, old, or of poor quality may have a lower germination rate.
- Soil moisture: Adequate soil moisture is crucial for germination. Seeds need sufficient moisture to absorb and activate enzymes, which initiate the germination process.
- Soil temperature: The temperature of the soil also impacts germination. Wheat seeds germinate best in soil temperatures ranging from 10°c to 30°c (50°f to 86°f).
- Oxygen availability: Like all living organisms, wheat seeds require oxygen for metabolic processes. Oxygen availability in the soil is crucial for successful germination.
- Light exposure: While some seeds require light for germination, wheat seeds do not. They can germinate effectively in the presence or absence of light.
Importance Of Soil Moisture And Temperature
Soil moisture and temperature are two crucial factors that significantly influence the germination of wheat seeds.
- Soil moisture: Adequate soil moisture is essential for the germination process as it softens the seed coat, allowing water uptake. It also provides the necessary hydration for cellular activities, enzyme activation, and the growth of the root and shoot system.
- Soil temperature: The temperature of the soil affects the speed and efficiency of germination. Ideal soil temperatures promote enzyme activity and metabolic processes necessary for seedling development.
Understanding the germination process of wheat seeds is vital for successful crop production. Factors such as seed quality, soil moisture, and temperature have a direct impact on the germination process. Providing optimal conditions for germination ensures healthy seedlings, contributing to higher yield potential.
Vegetative Stage: Leaf And Stem Development
The vegetative stage is a critical phase in the growth of wheat plants, where the focus shifts towards leaf and stem development. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring optimal growth and maximizing yields. In this section, we will explore the key elements related to the vegetative stage, including leaf development, stem growth, and nutrient requirements for robust vegetative growth.
Leaf Development In Wheat Plants
- Leaves play a vital role in the growth and development of wheat plants, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis and produce energy. Here are some key points regarding leaf development in wheat plants:
- Leaf emergence: The first leaves that appear in the vegetative stage are known as the “coleoptile leaves,” which push through the soil to reach the surface. Gradually, additional leaves unfurl, with newer leaves appearing from the crown of the plant.
- Leaf structure: Wheat leaves are elongated and linear, with parallel veins running through them. They are typically green due to the presence of chlorophyll, which facilitates photosynthesis.
- Leaf growth: During the vegetative stage, leaves continue to grow in size and increase in number. This growth stage is crucial for building a strong leaf canopy that can capture sunlight effectively.
Stem Growth During The Vegetative Stage
- Alongside leaf development, wheat plants also undergo significant stem growth during the vegetative stage. Consider the following points about stem growth:
- Stem elongation: As the vegetative stage progresses, wheat plants experience elongation of the stem. This growth allows the leaves to reach optimal exposure to sunlight, facilitating efficient photosynthesis.
- Internode length: Internodes, the segments between leaves on the stem, become longer during stem growth. The lengthening of internodes contributes to the overall height of the wheat plant.
- Tillering: Wheat plants also produce additional stems known as tillers during the vegetative stage. Tillers emerge from the base of the main stem, contributing to the plant’s overall biomass.
Nutrient Needs For Optimal Vegetative Growth
- To support healthy vegetative growth, wheat plants require specific nutrients. Here are some key nutrient needs during the vegetative stage:
- Nitrogen (n): Nitrogen is vital for promoting vigorous vegetative growth in wheat plants. It aids in the development of leaves, stems, and tillers. Adequate nitrogen availability is crucial to ensure optimal plant growth and maximize yield potential.
- Phosphorus (p): Phosphorus plays a critical role in root development and overall plant growth. It is essential for energy transfer, enzyme activity, and photosynthesis. Adequate phosphorus availability promotes robust root and shoot growth during the vegetative stage.
- Potassium (k): Potassium is involved in numerous physiological processes within the plant, including water regulation, enzyme activation, and nutrient transport. During the vegetative stage, an adequate supply of potassium supports strong stem and leaf development.
The vegetative stage of wheat growth is characterized by significant leaf and stem development. Understanding the dynamics of leaf emergence, stem elongation, and tillering is crucial for optimizing plant growth. Additionally, providing the necessary nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, is essential for ensuring healthy and productive vegetative growth.
By focusing on these aspects, farmers can set the stage for successful wheat crop development.
Reproductive Stage: Flowering And Grain Development
Flowering And Pollination In Wheat
Flowering is a critical stage in the growth of wheat, marking the transition from vegetative to reproductive growth. During this period, the wheat plants produce flowers that undergo the process of pollination. Here’s what you need to know about flowering and pollination in wheat:
- Wheat flowers are small and inconspicuous, clustered together in spikelets on the wheat head.
- The flowering stage typically occurs when the wheat plants are 50-75% of their final height.
- The flowers in each spikelet consist of the ovary, stigma, and stamens, which are responsible for the reproductive process.
- Wheat plants rely on external agents, such as wind or insects, for pollination.
- Pollen from the stamens is released and carried by wind or insects to the stigma of each flower.
- Successful pollination of wheat flowers leads to the development of ovules, which will eventually become the grains.
Grain Development And Fertilization Process
After successful pollination, the wheat flowers enter the grain development and fertilization process. This stage is crucial for the formation and maturity of grains. Here are the key points to understand about grain development and fertilization in wheat:
- Shortly after pollination, fertilization occurs as the pollen grains grow tubes that reach the ovules in the flower’s ovary.
- Each fertilized ovule develops into a kernel of wheat, which contains an embryo and endosperm that will nourish the developing plant.
- The grains undergo a process called grain fill, during which the embryo and endosperm grow and accumulate starch, proteins, and other nutrients.
- Grain filling is a critical period that requires optimal environmental conditions, especially for temperature and moisture.
- The length of the grain filling period varies based on the wheat variety and environmental factors.
- As the grains mature, the plants redirect their resources towards grain development, leading to changes in the plant’s appearance.
Yield Determinants During Reproductive Stage
Several factors influence wheat yield during the reproductive stage. Understanding these yield determinants can help farmers optimize their farming practices. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Adequate water availability during flowering and grain development is crucial for successful pollination and grain fill.
- Temperature plays a vital role in influencing the duration and efficiency of flowering and fertilization processes.
- The availability of nutrients, particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, affects grain development and yield.
- Wheat varieties with improved genetic traits, such as disease resistance and higher grain-setting ability, can enhance yield potential.
- Pest and disease management during the reproductive stage is crucial to minimize yield losses.
- The overall plant health and vigor, as well as the absence of stresses like drought or excessive heat, contribute to optimal yield during this stage.
By understanding the stages of flowering and grain development in wheat, as well as the key factors influencing yield during the reproductive stage, farmers can make informed decisions to maximize their wheat harvest. Planning irrigation, nutrient management, and pest control strategies accordingly can significantly enhance wheat productivity.
Maturation And Harvest Stage: Ripening And Harvesting The Wheat
At the maturation and harvest stage of the wheat growth cycle, the focus shifts to the ripening and harvesting of the wheat. Understanding the ripening process, indicators of crop maturity, and the optimal time and techniques for harvesting is crucial to ensure a successful harvest.
Let’s delve into these aspects in more detail:
Ripening Process Of Wheat Grains
During the ripening process, the wheat grains go through notable changes. Here’s a breakdown of the ripening process of wheat grains:
- Milk stage: At this stage, the wheat grains are pale and milky in appearance. They contain a high amount of moisture and are not yet ready for harvesting.
- Dough stage: As the grains progress to the dough stage, they become firmer and harder. The moisture content decreases, and the grains begin to exhibit a yellowish color.
- Ripening stage: In the ripening stage, the wheat grains turn golden brown and fully mature. They become hard and dry, indicating their readiness for harvesting.
Indicators Of Wheat Crop Maturity
To determine the maturity of the wheat crop, farmers observe several indicators. These indicators help them gauge the crop’s readiness for harvesting. Here are some indicators that signify the maturity of wheat crop:
- Color change: The color of the crop changes from green to golden brown as it approaches maturity.
- Firmness: The firmness of the wheat heads increases when they reach maturity. They become difficult to squeeze between fingers.
- Kernel hardness: The hardness of the wheat kernels intensifies as they mature. Fully mature kernels are firm and not easily dented.
- Moisture content: The moisture content of mature wheat grains is lower compared to earlier stages. It is crucial to assess the moisture content before harvesting.
Optimal Harvest Time And Techniques
To achieve the best yield and quality, determining the optimal harvest time for wheat is crucial. Consider these factors when deciding when to harvest:
- Moisture level: Harvesting wheat when the moisture content is around 13-14% is ideal. This ensures better grain quality and minimizes post-harvest losses.
- Weather conditions: Wait for a stretch of dry weather to ensure the wheat is adequately dry for harvesting and minimize the risk of quality degradation or sprouting.
- Field monitoring: Regularly monitor the crop’s maturity using indicators mentioned earlier to ensure you harvest at the optimal time.
- Harvesting techniques: Harvesting techniques vary depending on the size of the farm and available machinery. Common techniques include using combine harvesters or traditional methods like cutting with sickles and threshing.
Remember, proper timing and careful techniques are essential for a successful wheat harvest. By paying attention to the ripening process of wheat grains, understanding indicators of crop maturity, and considering the optimal time and techniques for harvesting, you can maximize your yield and ensure high-quality wheat.
Environmental Factors Affecting Wheat Growth Stages
Environmental Factors Affecting Wheat Growth
The growth of wheat plants is influenced by various environmental factors throughout its growth stages. Understanding these factors is crucial for successful wheat cultivation. In this section, we will explore three key environmental factors that significantly impact wheat growth: temperature, moisture and drought stress, and light and photoperiod.
Impact Of Temperature On Wheat Growth
Temperature plays a vital role in determining the growth and development of wheat crops. Here are some key points to consider:
- Optimum temperature range: Wheat plants typically thrive in temperatures between 15°c and 20°c. This range promotes optimal growth and leads to higher grain yield.
- Chilling injury: Exposing wheat plants to extremely low temperatures can cause chilling injury. This leads to slower growth, reduced tillering, and even the death of young plants.
- Heat stress: High temperatures above 30°c during the reproductive stage can adversely affect wheat productivity. Heat stress can lead to reduced grain yield, poor grain quality, and delayed maturity.
Effects Of Moisture And Drought Stress
Adequate moisture levels are essential for healthy wheat growth. However, drought stress can severely impact wheat crops. Consider the following points:
- Water requirement: Wheat plants require ample moisture during their growth stages. Adequate water supply ensures optimal photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and grain development.
- Drought stress: Insufficient water availability can result in drought stress. This condition leads to reduced photosynthesis, stunted growth, decreased tillering, and ultimately lower grain yield.
- Drought tolerance: Developing drought-tolerant wheat varieties is crucial to combat water scarcity. These varieties exhibit characteristics that allow them to withstand prolonged periods of drought and maintain relatively stable growth.
Influence Of Light And Photoperiod
Light and photoperiod greatly influence the growth and development of wheat plants. Consider the following points:
- Photoperiod sensitivity: Wheat is classified into three photoperiod groups: long-day, short-day, and day-neutral. These groups determine the plant’s sensitivity to day length and influence the timing of development stages.
- Vegetative growth: Sufficient light is essential for vigorous vegetative growth in wheat. Adequate sunlight promotes robust tillering, leaf development, and overall plant health.
- Flowering and grain development: Light also affects the timing of wheat flowering and grain development. The duration of darkness and light exposure influences the transition to reproductive stages and subsequent grain filling.
The environmental factors of temperature, moisture and drought stress, and light and photoperiod significantly impact the growth stages of wheat. Understanding how these factors influence wheat crops allows farmers to make informed decisions to optimize cultivation practices and maximize grain yield.
Common Pests And Diseases At Different Growth Stages
Wheat Growth Stages: Common Pests And Diseases At Different Growth Stages
Wheat, a crucial cereal crop, goes through distinct growth stages from germination to maturation. At each stage, various pests and diseases pose significant threats to the wheat plant’s health and productivity. By understanding these common pests and diseases and their corresponding growth stages, farmers can implement proactive measures to protect their wheat crops.
In this blog post, we will explore the pest threats in the germination and seedling stages, diseases and fungal infections during vegetative growth, and pests and pathogens during reproductive and maturation stages.
Pest Threats In Germination And Seedling Stages:
During the early growth stages of wheat, germination and seedling, several pests can potentially hinder the plant’s overall development. Here are some common pest threats:
- Aphids: Small, sap-sucking insects that can cause stunted growth and transmit viral diseases.
- Wireworms: Larvae of click beetles that feed on germinating seeds, leading to poor establishment.
- Armyworms: Larvae of certain moth species that can consume young wheat plants, causing severe defoliation.
- Cutworms: Nocturnal caterpillars that feed primarily on young seedlings, often cutting them near ground level.
- Slugs and snails: These mollusks can damage leaves and stems, resulting in reduced vigor and growth.
Diseases And Fungal Infections During Vegetative Growth:
As wheat enters the vegetative growth stage, diseases and fungal infections become a major concern. Here are some of the prevalent ones during this period:
- Leaf rust: A fungal disease that appears as orange or reddish-brown pustules on leaves, reducing photosynthetic capacity.
- Powdery mildew: A widespread fungal infection resulting in a white powdery coating on leaves, affecting plant growth and yield.
- Septoria leaf blotch: A fungal disease characterized by small, dark spots with yellow halos on leaves, potentially leading to defoliation.
- Fusarium head blight: A fungal infection that affects the wheat head, causing shriveled grains and reduced yield.
- Tan spot: A fungal disease marked by tan lesions on leaves, resulting in reduced photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Pests And Pathogens During Reproductive And Maturation Stages:
During the reproductive and maturation stages of wheat, pests and pathogens can severely impact crop productivity. Here are some significant threats:
- Hessian fly: A destructive pest that attacks wheat stems and leaves, causing stunted growth and yield reduction.
- Wheat stem sawfly: Larvae of this insect tunnel into wheat stems, weakening them and increasing the risk of lodging.
- Earwigs: These nocturnal insects can feed on wheat kernels, leading to reduced grain quality and yield.
- Wheat curl mite: A microscopic pest that spreads viruses and can cause stunted growth and yield loss.
- Ergot: A fungal disease that affects the wheat head, producing dark purple or black sclerotia, which are toxic to humans and animals if consumed.
By understanding the specific pests and diseases that are commonly associated with each growth stage, farmers can take timely and appropriate actions to protect their wheat crops and ensure optimal yield. Regular scouting, implementing integrated pest management strategies, and selecting resistant wheat varieties are among the key approaches to mitigate the risks posed by these pests and diseases.
Remember to consult local agricultural experts or extension services for tailored advice based on your region and specific cropping practices.
Best Practices For Monitoring And Managing Wheat Growth Stages
Importance Of Regular Crop Monitoring
Regular monitoring of wheat growth stages is crucial for ensuring optimal crop management and maximizing yields. By closely observing the growth stages of wheat, farmers can identify potential issues, make informed decisions, and implement necessary interventions to promote healthy growth.
Here are the key reasons why regular crop monitoring is essential:
- Early detection of pests and diseases: Monitoring the growth stages allows farmers to identify any signs of pest infestations or diseases early on. This enables them to take prompt action and prevent the spread of harmful organisms, protecting the crop from significant damage.
- Timely nutrient management: By monitoring the growth stages, farmers can assess the nutrient requirements of the wheat plants and provide timely fertilization. This ensures that the crop receives the necessary nutrients at each stage, supporting healthy growth and improved yield potential.
- Effective irrigation management: Monitoring the growth stages helps farmers determine the optimal irrigation requirements for the wheat crop. Proper irrigation timing and dosage based on growth stages prevent overwatering or under-watering, minimizing the risk of water stress and maximizing water-use efficiency.
- Yield forecasting: Regular monitoring provides valuable insights into the crop’s progress, allowing farmers to estimate potential yield levels. This information enables better planning for harvesting, storage, and marketing, optimizing the overall profitability of the wheat crop.
Techniques For Assessing Wheat Growth Stages
Accurate assessment of wheat growth stages is essential for effective crop management. Various techniques can be used to monitor and evaluate the growth stages of wheat. Here are the commonly employed techniques:
- Visual observation: This involves physically inspecting the wheat plants and examining their characteristics and developmental changes. Visual cues such as leaf appearance, stem elongation, flowering, and grain filling are used to determine the growth stage.
- Phenological scales: Phenological scales provide standardized descriptions and criteria to assess the growth stages of wheat based on observable plant characteristics. These scales enable consistent and comparable growth stage assessments across different regions and time periods.
- Remote sensing: Advanced technologies such as satellite imagery and drones equipped with multispectral sensors can be used to capture data on crop growth and development. By analyzing the collected data, farmers can assess the growth stages of wheat and identify spatial variability within the field.
Strategies For Effective Management Of Growth Stages
Managing wheat growth stages requires comprehensive planning and implementation of appropriate strategies. Here are some effective strategies for managing the growth stages of wheat:
- Timely planting: Ensuring timely planting allows the wheat crop to establish and develop at the right time, promoting uniform growth and reducing the risk of yield loss.
- Disease and pest management: Implementing preventive measures and timely application of suitable pesticides or fungicides can help control diseases and pests, safeguarding the health and productivity of the wheat crop.
- Fertilizer application: Applying fertilizers at the recommended growth stages ensures that the wheat plants receive the necessary nutrients to support their development. The timing and dosage of fertilizers should be aligned with the growth stage requirements.
- Irrigation management: Understanding the water needs at different growth stages is crucial for efficient irrigation management. Providing the right amount of water at the right time promotes optimal growth, prevents water stress, and minimizes water wastage.
- Weed control: Regular monitoring of weed growth stages is important to identify and control the weeds in a timely manner. Effective weed management techniques such as manual removal, herbicide application, or mulching should be implemented to prevent weed competition with the wheat crop.
By following these best practices, farmers can effectively monitor and manage the growth stages of wheat, ensuring healthy crop development, and maximizing overall yield potential.
Frequently Asked Questions On Wheat Growth Stages
What Are The Different Growth Stages Of Wheat?
Wheat goes through several growth stages: germination, tillering, stem elongation, booting, heading, flowering, milk development, dough development, and maturity. Each stage has specific characteristics and requirements.
How Long Does It Take For Wheat To Reach Maturity?
The time it takes for wheat to reach maturity varies depending on the variety, growing conditions, and region. On average, wheat takes about 110-130 days from planting to maturity. However, some varieties may have shorter or longer maturity periods.
What Is The Importance Of Wheat Growth Stages?
Understanding the growth stages of wheat is crucial for proper management and maximizing yield. It helps farmers determine the right time for fertilization, irrigation, pest control, and harvesting. Each growth stage has specific needs that, when met, can lead to healthier plants and better grain production.
Conclusion
Understanding the different growth stages of wheat is crucial for farmers and researchers alike. By identifying these stages, they can make well-informed decisions regarding planting, fertilization, and pest control. The initial stage, germination, marks the beginning of the wheat plant’s life cycle, followed by tillering, when multiple stems emerge from a single seed.
During the stem elongation phase, the wheat plant grows rapidly, and it is during this time that farmers must pay attention to timely nitrogen application to maximize yield potential. Heading and flowering stages are critical for pollination and grain production, while the milk and dough stages indicate the development of the grain.
Lastly, the ripening and maturity stages signal that the crop is ready for harvest. By understanding and monitoring these growth stages, farmers can ensure optimal crop management and improve their overall yield and profitability.
