Plants grow towards sunlight through a process called phototropism. Photoreceptors in plant cells detect light, triggering growth towards the light source.
When plants grow towards sunlight, it’s because of a phenomenon called phototropism. This process enables them to maximize their exposure to sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis and overall growth. Photoreceptors within plant cells are responsible for detecting light, prompting the plant to redirect its growth towards the light source.
This adaptive process ensures that plants receive the necessary sunlight for their energy needs, ultimately contributing to their survival and vitality. Understanding how plants respond to light is fundamental in optimizing agricultural practices and enhancing plant growth in various environments.
Why Plants Grow Toward Sunlight
Have you ever wondered why plants always seem to lean toward the sunlight? It’s a fascinating phenomenon that showcases the incredible adaptability of these green wonders. In this blog post, we’ll explore the reasons behind why plants grow toward sunlight, diving into the concept of phototropism and the crucial role sunlight plays in their growth.
Phototropism And Its Role
Phototropism is the scientific term used to describe the phenomenon of plants growing toward light. It is a crucial mechanism that allows plants to optimize their energy intake by positioning their leaves, stems, and flowers in the direction of the sun.
Phototropism occurs due to the hormone auxin, which is produced in the plant’s tip, specifically in the meristematic tissue. When exposed to light, auxin redistributes itself, causing the cells on the shaded side of the plant to elongate. As a result, the stem bends toward the light source.
Importance Of Sunlight For Plants
Sunlight is like the life force of plants, playing a vital role in their growth and development. Here are a few key reasons why sunlight is so important:
- Photosynthesis: Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Through photosynthesis, plants produce glucose and oxygen, enabling them to grow and thrive.
- Energy Source: Sunlight is the primary source of energy for plants. It provides the necessary fuel for various metabolic processes, allowing plants to carry out crucial functions such as nutrient absorption, respiration, and reproduction.
- Directional Growth: By growing toward sunlight, plants maximize their exposure to this valuable resource, enabling them to capture more energy for photosynthesis and maintain overall health.
- Leaf Orientation: Sunlight determines the orientation and arrangement of leaves on the plant. The positioning of leaves ensures that each leaf receives an optimal amount of sunlight, allowing for efficient photosynthesis.
Without sunlight, plants would struggle to survive and thrive. Lack of sunlight can lead to stunted growth, chlorosis (yellowing of leaves), and overall weakened health. In essence, sunlight is the key ingredient that enables plants to harness energy and carry out essential biological processes.

Credit: www.thoughtco.com
Mechanism Of Plant Growth Toward Sunlight
When plants grow toward sunlight, it’s not just random movement. There is a sophisticated mechanism in place that allows them to sense and respond to the sun’s rays. Understanding the mechanism of plant growth toward sunlight can help us appreciate the incredible precision and adaptability of the plant kingdom.
Role Of Auxin Hormone
The role of the auxin hormone is crucial in the mechanism of plant growth toward sunlight. Auxin hormone is primarily responsible for cell elongation. When a plant is exposed to sunlight, auxin distribution within the plant becomes unequal, causing the cells on the shaded side to elongate more than those on the sunlit side. This unequal growth leads to bending or curvature toward the light source.
Gene Expression And Directional Growth
In addition to the role of auxin, gene expression also plays a significant part in directional growth toward sunlight. When light hits a plant, specific genes are activated, prompting the production of proteins that are crucial for growth, especially in the direction of the light source. This intricate process allows the plant to execute a precise response to the sunlight, ensuring optimal exposure for photosynthesis.
Adaptations In Plants To Maximize Sunlight Exposure
Adaptations in plants to maximize sunlight exposure are remarkable examples of nature’s ingenuity. Plants have evolved various strategies to ensure they receive the maximum amount of sunlight, which is essential for their photosynthesis and overall growth. Leaf orientation and structure and stem elongation and bending are two key adaptations that enable plants to optimize their exposure to sunlight.
Leaf Orientation And Structure
Plants have developed specific leaf orientations and structures to effectively capture sunlight. Some leaves orient themselves to face the sun at all times of the day. This allows for consistent access to sunlight and enhances the plant’s photosynthesis process.
Stem Elongation And Bending
Stem elongation and bending are critical features that aid in maximizing sunlight exposure for plants. When a plant’s stem elongates, it can lift the leaves to higher positions, thereby allowing more sunlight to reach the lower leaves. Additionally, the ability of stems to bend allows plants to reposition themselves towards the sun, ensuring continuous access to sunlight throughout the day.
Response To Different Light Conditions
Response to Different Light Conditions
Plants are incredibly adaptable organisms and have developed unique mechanisms to respond to different light conditions. When it comes to sunlight, their response is particularly interesting. They have the ability to grow towards the light, ensuring they receive the maximum amount of energy for photosynthesis. In this section, we will explore the effect of shade on plant growth and the concept of photoperiodism and flowering.
Effect Of Shade On Plant Growth
Shade plays a crucial role in shaping plant growth and development. When plants are deprived of sunlight or placed in low-light conditions, they undergo a series of physiological changes to survive. Here are some key effects of shade on plant growth:
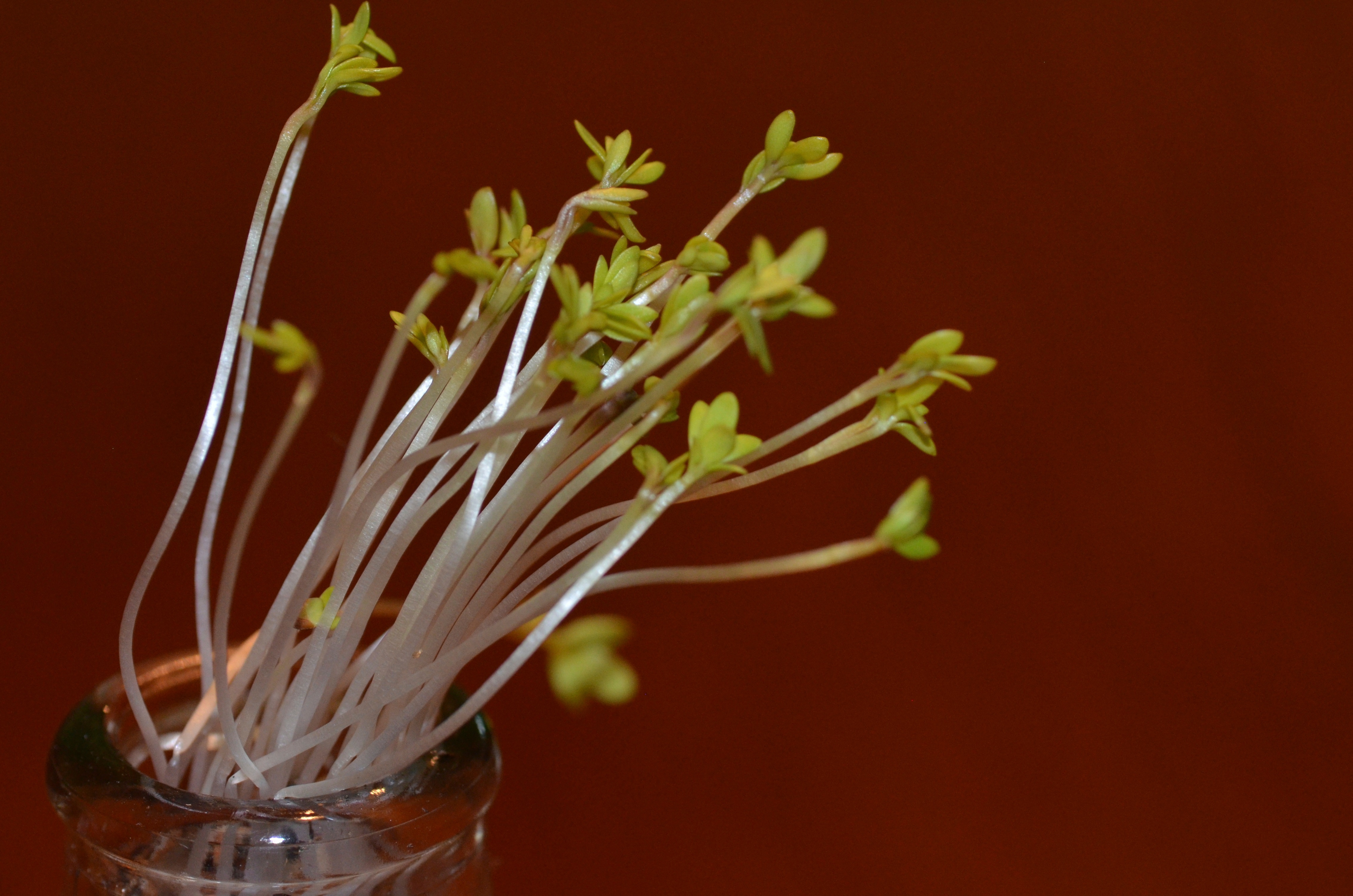
- Increased stem elongation: In the absence of adequate sunlight, plants exhibit a phenomenon called etiolation. This causes their stems to grow longer and thinner as they stretch towards available light sources.
- Reduced leaf size: Leaves play a vital role in capturing sunlight for photosynthesis. In low-light environments, plants allocate fewer resources to leaf development, resulting in smaller and thinner leaves.
- Altered leaf color: Without sufficient sunlight, plants produce less chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color of leaves. This leads to leaves appearing pale or yellowish.
- Delayed flowering: Shade can significantly affect the timing of flowering in plants. Extended periods of shade may delay or even prevent the development of flowers.
Photoperiodism And Flowering
Plants possess an internal biological clock that allows them to measure the duration of light and darkness. This phenomenon is known as photoperiodism and plays a critical role in triggering flowering. Here’s how it works:
- Short-day plants: These plants require longer periods of darkness to initiate the flowering process. They typically bloom when nights are longer than a certain critical duration.
- Long-day plants: In contrast to short-day plants, long-day plants bloom when they are exposed to shorter periods of darkness. They require nights shorter than a specific critical duration to begin flowering.
- Day-neutral plants: Unlike short-day and long-day plants, day-neutral plants are not significantly influenced by light duration. They can initiate flowering despite variations in day length.
This innate ability of plants to respond to different light conditions is essential for their survival and reproductive success. Understanding these responses can help us optimize plant growth in various environments and create ideal conditions for cultivation.
Human Applications And Importance
Plants instinctively lean towards sunlight to undergo photosynthesis, their process for converting light into energy and nutrients. This movement, known as phototropism, is crucial for their growth and survival. Sunlight serves as a vital catalyst for plant development, enabling them to thrive in their environment.
Utilizing Phototropism In Agriculture
Plants growing towards sunlight crucial to maximize agricultural productivity can lead to healthier crops.Designing Sunlight Strategies For Indoor Plants
Understanding how plants respond to light can be used in indoor settings to promote optimal growth.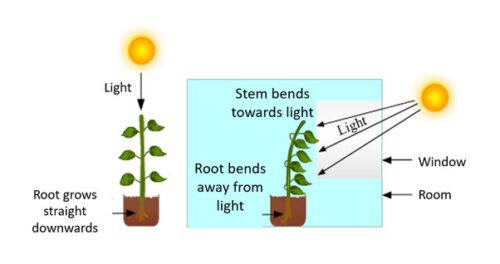
Credit: www.quora.com

Credit: phys.org
Frequently Asked Questions On What Happens When Plants Grow Toward Sunlight?
What Happens When A Plant Is Exposed To Sunlight?
When plants are exposed to sunlight, they undergo photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy.
What Is It Called When Plants Grow Toward Sunlight?
Plants growing toward sunlight is called phototropism. It’s their natural response to seek light for photosynthesis.
Why Do Plants Grow Toward The Sunlight Give Reason?
Plants grow toward sunlight because they need it for photosynthesis, their food-making process. Sunlight provides energy for growth.
Why Is Sunlight Important For Plant Growth?
Sunlight is crucial for plant growth because it provides the energy needed for photosynthesis. This process converts sunlight into chemical energy, allowing plants to produce food. Without sunlight, plants would struggle to grow and thrive.
Conclusion
As sunlight plays a crucial role in the growth of plants, they have evolved various mechanisms to ensure they receive sufficient light. Through phototropism, plants are able to bend or grow towards sunlight, optimizing photosynthesis. This process allows them to produce the energy they need to survive and thrive.
Understanding how plants respond to light can aid in their cultivation and enhance agricultural practices. So, next time you see a plant stretching towards the sun, marvel at the wonders of nature’s ingenuity.
