Plant root growth refers to the process by which the underground part of a plant develops and extends. It involves the formation of new roots, elongation of existing roots, and branching to support nutrient absorption and anchorage of the plant in the soil.
For a plant to survive and thrive, healthy root growth is essential. The roots play a vital role in absorbing water and minerals from the soil, providing stability to the plant, and storing reserves. The process of root growth begins with the germination of the seed and continues throughout the plant’s life, with roots constantly exploring the soil in search of resources.
Factors such as temperature, moisture, soil composition, and the presence of symbiotic organisms influence root growth. Understanding the meaning of plant root growth is crucial for gardeners, farmers, and scientists, as it provides insights into plant health and productivity. By nurturing and supporting root growth, we can enhance the overall well-being of plants and optimize their growth potential.
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
The Basics Of Plant Root Growth
Plant root growth is essential to the overall health and development of plants. Understanding the fundamentals of root growth is crucial for successful gardening and agriculture.
The Role Of Roots In Plants
Roots anchor plants in the soil, absorb water and nutrients, and store food for growth.
Root Structure And Function
- Primary roots grow downward while lateral roots extend horizontally.
- The root tip contains the root cap that protects the growing tip.
- Root hairs increase the surface area for water and nutrient absorption.
Roots are the foundation of plant growth, providing stability and vital functions to support plant life.
Factors Affecting Plant Root Growth
There are several factors that can have a significant impact on the growth of plant roots. Understanding these factors is crucial for gardeners and farmers who want to cultivate healthy and thriving plants. In this section, we will explore the various environmental and soil conditions that affect plant root growth.
Environmental Factors
The environment plays a crucial role in determining how plants grow and develop. Here are some key environmental factors that affect plant root growth:
- Light: Plants need adequate sunlight to fuel the process of photosynthesis, which in turn supports root growth. Insufficient light can lead to stunted root development.
- Temperature: Different plants have different temperature preferences, but generally, a moderate and consistent temperature is ideal for root growth. Extreme temperatures can stress plants and hinder their root development.
- Humidity: Some plants prefer higher humidity levels, while others can tolerate drier conditions. The right balance of humidity is important for root growth and overall plant health.
- Wind: Strong winds can dry out the soil and cause excessive water loss through evaporation, making it difficult for plant roots to absorb water and nutrients effectively.
Soil Conditions
The quality and composition of the soil are crucial factors that influence plant root growth. Here are some important soil conditions to consider:
- Soil Texture: The texture of the soil, such as its relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay, affects water drainage and nutrient availability. Well-draining soil with a good balance of these components promotes healthy root growth.
- Soil pH: Different plants have different pH preferences. Acidic or alkaline soil can hamper nutrient absorption and hinder root growth.
- Soil Moisture: Adequate soil moisture is essential for plant roots to absorb water and nutrients. Both waterlogged and excessively dry conditions can stunt root growth.
- Soil Structure: A loose, crumbly soil structure is ideal for root penetration. Compacted soil, on the other hand, can restrict root growth and limit nutrient uptake.
- Soil Nutrients: Plants require various nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, for healthy root development. Nutrient deficiencies or imbalances can impede root growth.
Stages Of Plant Root Growth
Plant root growth refers to the process by which roots of a plant develop and expand. It progresses through distinct stages, starting with the initial emergence of the radicle, followed by primary and secondary root growth. As the roots elongate and branch out, they anchor the plant and absorb essential nutrients and water from the soil.
Understanding the stages of plant root growth is essential for anyone seeking to cultivate healthy and thriving plants. The roots play a vital role in facilitating the uptake of water, nutrients, and anchoring the plants in the soil. Let’s explore the two key stages of plant root growth: seed germination and early growth, as well as root development and maturation.
Seed Germination And Early Growth
Seed germination marks the beginning of the plant’s life cycle. As the seed absorbs water, it swells and eventually ruptures, allowing the embryonic root, known as the radicle, to emerge. The radicle grows downward, seeking moisture and nutrients within the soil. Gradually, the root system undergoes primary growth, which extends the length of the root through cell division and elongation.
During this stage, secondary roots, also called lateral roots, begin to form as tiny plant hairs known as root hairs appear along the root’s surface. These root hairs enhance the root’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Seedlings rely heavily on these initial root structures to gather the resources needed for growth and development.
As the plant progresses through the early growth stage, the root system grows more robust, establishing a strong foundation for the plant to thrive. The root extends deeper into the ground, continuously exploring the soil for essential nutrients and moisture, ensuring the plant’s survival.
Root Development And Maturation
Root development and maturation signify the second stage of plant root growth. As the plant matures, the root system becomes more complex and extensive. The primary root, or taproot, further branches out into secondary roots, which then give rise to tertiary roots.
This intricate network of roots expands in multiple directions, creating a stronger grip within the soil and increasing the plant’s ability to acquire nutrients and water. The secondary and tertiary roots grow laterally, spreading outwards from the initial root, anchoring the plant firmly into the ground.
As the root system further matures, it not only ensures the plant’s structural stability but also plays a crucial role in storing nutrients for future use. The root tissues undergo cell differentiation, forming specialized structures such as root caps, root cortex, and vascular tissues, which enable efficient nutrient transport across the plant.
Throughout this stage, root hairs continue to develop and elongate, further enhancing the plant’s capacity to absorb water and necessary nutrients from the soil. The healthy and well-developed root system promotes overall plant growth and facilitates the efficient flow of vital resources.
Signs Of Healthy Plant Root Growth
Signs of Healthy Plant Root Growth:
Optimal Root System Characteristics
Healthy plant root growth exhibits optimal characteristics that are crucial for plant development.
Visible Plant Health Indicators
Signs of plant health are evident through observable indicators in the roots of the plant.
Promoting And Supporting Plant Root Growth
Understanding plant root growth is crucial for successful cultivation. Promoting and supporting plant root growth involves various techniques and strategies that contribute to the overall health and productivity of the plants. By implementing cultivation techniques and utilizing root growth enhancers, gardeners and farmers can optimize the development of strong and robust root systems, ultimately leading to improved plant vitality and yield.
Cultivation Techniques
Effective cultivation techniques play a significant role in promoting plant root growth. This includes proper soil preparation, adequate watering, and suitable planting depths. By loosening compacted soil, providing sufficient nutrients, and ensuring proper drainage, gardeners can create an optimal environment for root development. Furthermore, practicing crop rotation and using cover crops can help maintain soil structure and enhance root growth, leading to healthier and more resilient plants.
Use Of Root Growth Enhancers
The use of root growth enhancers can greatly influence the development of plant roots. These products, containing natural or synthetic compounds, are designed to stimulate root growth, improve nutrient uptake, and enhance overall plant vigor. Substances such as mycorrhizal fungi, humic acids, and cytokinins can be applied to the soil or directly to the roots to promote robust and extensive root systems. Incorporating root growth enhancers into regular plant care routines can result in stronger, more resilient plants with increased resistance to environmental stressors.

Credit: www.britannica.com
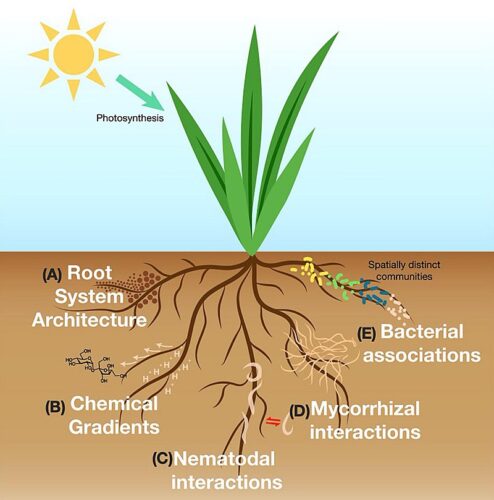
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Meaning Of Plant Root Growth?
What Is The Meaning Of Plant Roots?
Plant roots are essential structures that anchor the plant in soil, absorb water and nutrients, and provide stability for growth.
What Is The Role Of Roots In Plant Growth?
Roots play a crucial role in plant growth by anchoring the plant, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, and storing food. They provide stability, support, and enable the transport of water and minerals to other parts of the plant, aiding in its overall development and survival.
Is Root Growth Good?
Root growth is beneficial for plants as it allows them to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. It also provides stability to the plant by anchoring it in the ground. Adequate root growth is essential for the overall health and productivity of plants.
How Do You Get Good Root Growth?
For good root growth, provide proper drainage, nutrient-rich soil, adequate water, and sunlight. Avoid compacted soil and over-fertilization.
Conclusion
In understanding plant root growth, we uncover nature’s intricate processes. Roots are crucial for plant life, anchoring them, absorbing nutrients, and facilitating growth. By delving deeper into root systems, we appreciate the vitality they bring to the ecosystem. So, let’s continue exploring the wonders beneath the surface.
